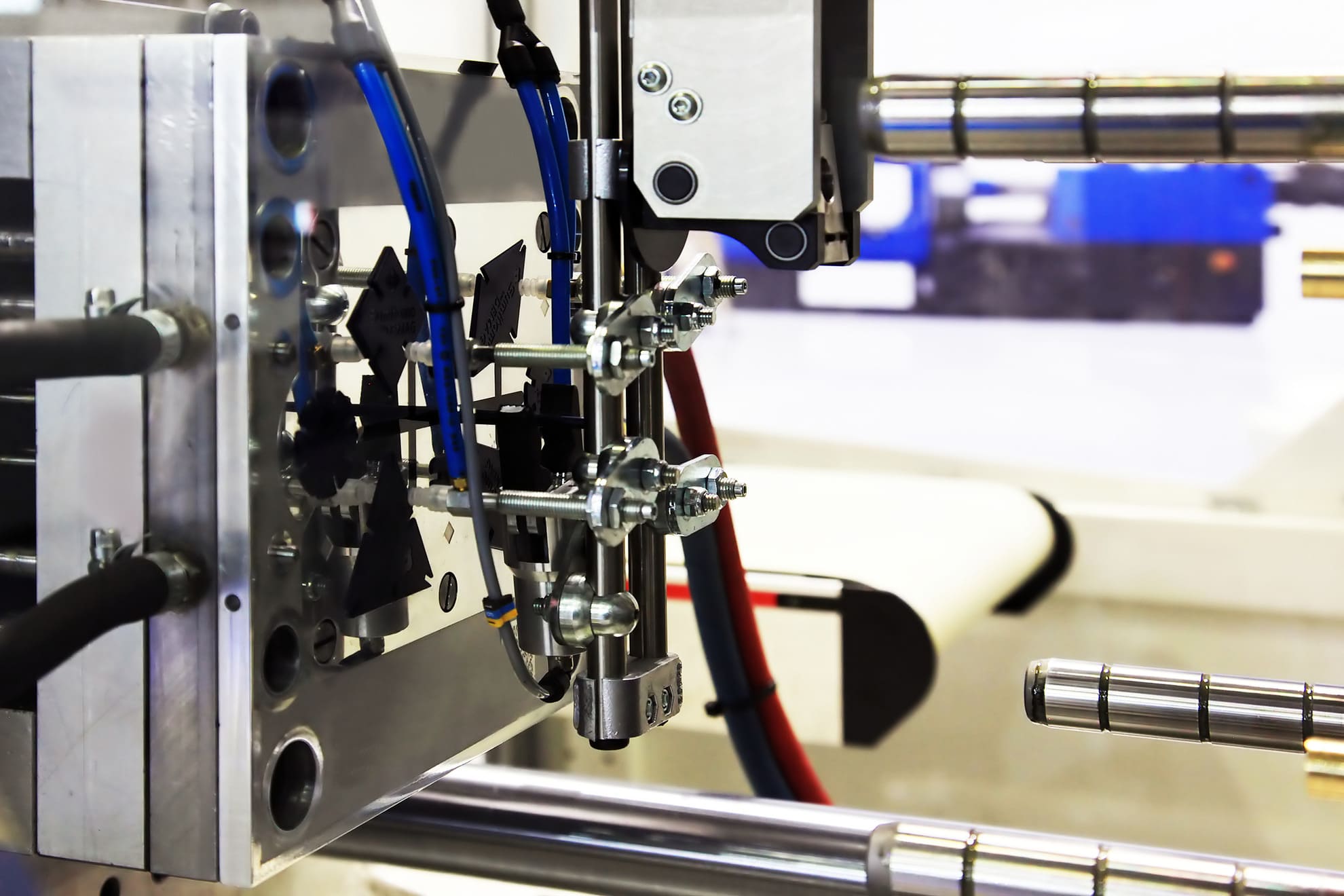
Overview of Custom Rubber and Polyurethane Molding Processes
Individuals often turn to a company specializing in moulded elastomeric products when they cannot find what they need. They know that with the help of polyurethane moulding, they can obtain plastic parts for their consumer goods or industrial needs. Thanks to the tight tolerances and complex geometries available with this production method, this is one option anyone should consider when needing parts of this type.
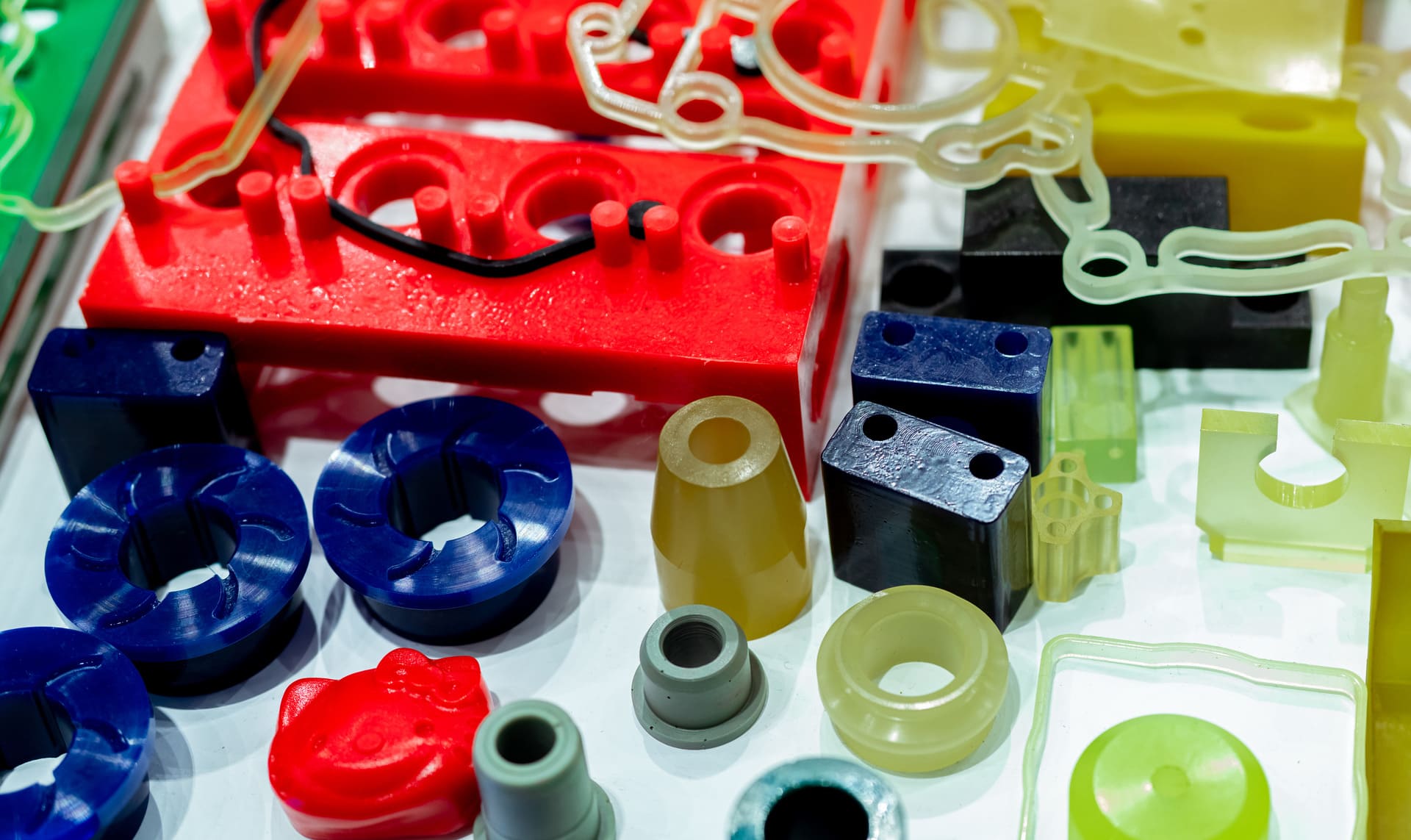
Polyurethane is a highly versatile material that yields different properties based on its formulation. The mechanical properties range from stiff and tight to soft and pliable. As a result, specific compounds can produce engineering-grade parts that deliver high performance. They are frequently found in the furnishings, construction, transportation, industrial, and manufacturing sectors. However, Custom Rubber and Polyurethane Molding may be needed to create the desired part. Why is polyurethane in high demand?
Polyurethane Properties
Polyurethane can be created to meet the project’s needs. Manufacturers use the Shore Hardness Scale to determine the hardness of the material. The Shore D scale is used to measure rigid and hard polyurethanes. They turn to the Shore A scale when they wish to measure a soft, semi-rigid polyurethane.
Furthermore, when polyurethane is used to create a part, the manufacturer can provide the desired level of abrasion resistance by altering the composition of the polyurethane resin. However, this is only one of several characteristics the manufacturer can alter. When creating custom polyurethane moulded parts, the manufacturer can control the tear strength, the impact strength, and more.
Moulding Techniques
Thanks to its flexibility, polyurethane can be moulded, shaped, or formed to meet the consumer’s needs. The manufacturer uses one of several techniques when creating these products. Injection moulding is commonly used for mouldings and can be used for thermoplastic and thermoset polyurethanes. Once it is moulded, the product is machined using the negative image of the desired product.
Reaction injection moulding is similar in many ways to injection moulding. The critical difference lies in the raw materials used. Manufacturers often choose this option when possible, as their costs are reduced.
Compressional moulding is ideal for large products. The mould is created in two pieces. The manufacturer then adds polyurethane in a predetermined weight. When the two halves are compressed, this polyurethane shapes the mould.
Rotational moulding is ideal for creating hollow pieces with no seams. Powdered polyurethane is loaded into a mould and heated while rotating, spreading the material throughout the inner surface of the mould. Once this process is complete, the product can cool before removal from the mould.
Blow moulding is also used to create hollow products. However, polyurethane is heated and placed in a tube. Compressed air inflates the polyurethane until it takes the shape of the mold. Once cooled, the mould is removed.
Casting
Casting is similar to injection moulding, but the mould is made of silicone rather than hard metal. This process is ideal for low to medium-volume products, as the mould wears quickly. However, this method is less expensive than using a mould made from metal.
Open Cast Molding
The most straightforward moulding technique is open-cast moulding. Manufacturers use this process for high-hardness polyurethane products. This rapid process allows for finished products in a few weeks. However, the resin and curative liquid must be at the correct temperature to solidify the heated liquid. Any material can be used with this moulding method, and the process is cost-effective.
Raw Material Options
Manufacturers find they can choose from a range of polyurethane components. Polyols and diisocyanates are the main components, and the manufacturer decides which curatives and additives to use in the formulation. Options include polyether, polyester, polycarbonates, aliphatic diisocyanates, aromatic diisocyanates, and various molecules.
Blowing agent options include chemical agents, physical ones, surfactants, catalysts, and more. Other products may also be used to create polyurethane.
For example, a manufacturer may use a degassing aid when creating products. As they mix the components of the polymer system, they must be aware that the mixing can lead to gases becoming trapped. These gases result in a lower-quality product. To avoid this issue, the manufacturer uses degassing aids to eliminate the trapped gases.
Polyurethanes may combust, which is of concern. This is especially true of polyurethane foams. As a result, manufacturers would be limited in using these products. To avoid this concern, the manufacturer uses flame-resistant polyurethanes when creating building insulation or parts for use in automobiles.
Manufacturers use colourants to alter a product’s colour. This process ensures that the polyurethane’s colour does not affect the product’s thermal and mechanical properties.
Finally, the coefficient of friction, or COF, of additives alters the coefficient of friction of the product. At times, a high COF is needed when sliding between surfaces. In contrast, a low COF is required when more friction is needed between materials. More challenging polyurethane products need a lower COF. The manufacturer can change the COF by altering the additive formulation.
Rubber Molding
Rubber moulding, unlike polyurethane moulding, has fewer options. Manufacturers use compression or injection moulding in many cases. They may also choose to use a combination of the two methods through a process known as transfer moulding. This process starts by converting raw material into a pre-form. The manufacturer places this pre-form in a pot before forcing the materials into the mould.
Polyurethane moulding is more complex than rubber moulding, as manufacturers have more options for the moulding process. However, both methods benefit manufacturers, depending on the product being created. Speak with a reputable provider to learn which material and method are needed. They can explain the benefits and drawbacks of each option and are an excellent resource for ensuring that suitable material methods are used.