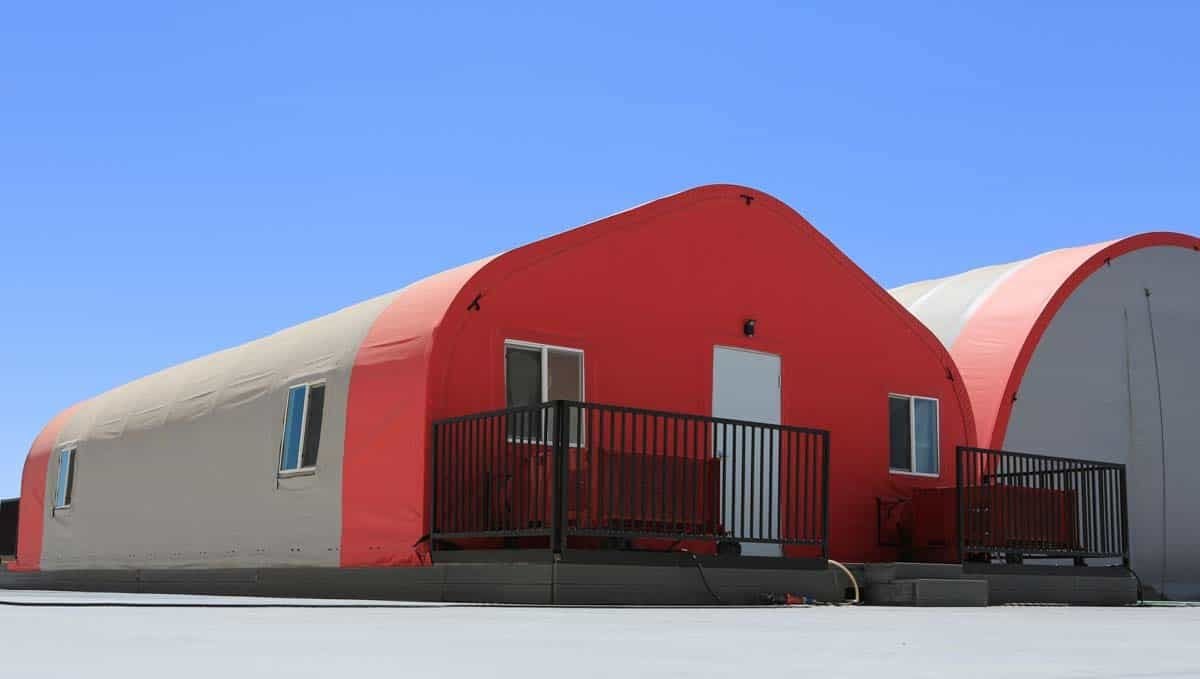
The Technology of How Pre-Engineered Structures Are Adapted for Different Environments Around the World
Pre-engineered buildings are transforming how communities and industries create functional space. They are adaptable to different environments, reflecting ingenuity in responding to differing global demands for efficiency.
Around the world, construction is faced with a trade-off among durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Advanced engineering has allowed engineers to design buildings to meet these demands. The designs are vital to corporations conducting commerce from snowy tundras to saltwater shores.
Engineering Economics and Efficiency
The key to this construction work is efficiency, such as using pre-engineered structures, which are precisely engineered at factories before being transported and assembled at the construction site. This is less wasteful and cheaper compared to conventionally constructed buildings.
Another advantage is flexibility. As it is transferred to warehouses, hangars, factories, and community facilities, these buildings can be adapted to meet a project’s individual requirements. This makes it possible to enlarge, change, and reconfigure with relative simplicity, making them attractive to firms with anticipated expansion or conversion.
Engineers can ensure that buildings meet stringent standards by employing superior-grade materials and state-of-the-art design software. This union of planning and technology not only makes construction easier and quicker but also provides reliability in the long run.
Succeeding in Extreme Environments
One of the most compelling arguments for pre-fabricated construction is its ability to perform in extreme climates. While it is hot and conditions are severe during the day and night in desert climates, insulation and reflective roof materials can keep interiors cooled and comfortable to work out of during the day with direct sunlight exposure.
Conversely, with Arctic or sub-Arctic-type climates, structural refinements are all about insulation and snow loads. The pitches can be modulated to prevent excessive snow buildup, and salty ice moisture is repelled by corrosion-resistant coatings. These details reveal engineers honing an average design to suit an uncommon environmental requirement.
Sites exposed to heavy rainfalls or flooding are equally supplied with customized solutions. Advanced foundations and water-resistant materials lessen the possibility of damage, and buildings are, therefore, always operational during seasonally recurring inclement weather circumstances. This versatility is proof enough to demonstrate that the same core technology can work everywhere around the world.
Structural Developments for Seismic and Coastal Locations
Seaside sites present challenges involving salt-enriched atmosphere, windy sites, and occasional storms. Pre-fabricated buildings are generally pre-coated to help resist rusting, and aerodynamic shapes help to reduce wind drag. This makes it possible to ensure buildings’ lifespan regardless of sites that test durability daily.
In seismic regions, innovation takes a different shape. Engineers create buildings with flexible connections, strengthened frames, and light construction to absorb and release seismic vibrations. These measures ensure buildings are safe and functional when rocked by earthquakes.
These examples show how the same base technology can be optimized to work in extremely different environments. Without starting from scratch, engineers merely adopt tried-and-tested design methods and adapt them to meet local needs.
Taking Into Account Local Sustainability Concerns
Sustainability is a key motivator in contemporary construction. Pre-engineered buildings are in step with this trend by minimizing materials wasted during manufacture and minimizing construction periods, thus reducing energy usage. These are all reasons why using pre-engineered buildings is an eco-friendly option.
Local environmental conditions also inform design. For instance, in locations with an abundance of renewable power, buildings can become at least partially powered by solar panels or wind turbines. In locations where natural ventilation is a wiser option, designs can feature large openings and ventilation strategies.
The combination of global standards and local demands enables these buildings to achieve ecological and economic benefits as well. That dual advantage is why there are so many industries moving towards this type of construction for permanent solutions.
Why Adaptive Designs Pay Off for Industries
Pre-engineered buildings are not confined to industrial use anymore. They are being used for schools and universities, clinics and hospitals, retail and shop facilities, and residential solutions today. They are varied and capable of allowing communities and businesses to benefit from technology.
The logistics industry is one of its biggest beneficiaries. Storage and delivery centers require large open spaces, and these buildings accommodate them well. Similarly, aviation relies greatly on swiftly made hangars and climate-changeable ones.
Pre-engineered construction is particularly valuable in the developing world because it is fast and inexpensive. The buildings can expediently supply schools, clinics, and shelters, and bring necessary infrastructure to those who are most in need. Pre-engineered construction is changing the built environment by marrying flexibility and accessibility.
Building for the World’s Future
The history of pre-engineered buildings is one of ingenuity and pragmatism. The ability to adapt to different climates, withstand ecological forces, and support global industries is a testament to their relevance to construction today. As the planet gazes towards its future with environmental challenges and growing infrastructure demand ahead, these buildings present a permanent, efficient, and sustainable direction for it all to go towards. They’re not buildings; they’re solutions engineered towards a globalized and transforming world.