How Deep Cycle Lithium Batteries Protect the Earth
- 1 Threats of Traditional Lead-Acid Batteries
- 1.1 Environmental Pollution:
- 1.2 Health Risks:
- 1.3 Inefficient Recycling:
- 1.4 Limited Energy Density:
- 1.5 Shorter Lifespan:
- 2 Lithium Battery’s contribution to Environmental Protection
- 3 How Lithium Deep Cycle Batteries Protect the Environment
- 3.1 Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
- 3.2 Efficient Energy Storage:
- 3.3 Extended Product Lifespan:
- 3.4 Minimal Environmental Impact:
- 3.5 Driving Sustainable Practices:
- 3.6 Promoting Circular Economy Principles:
- 4 Additional Ways to Support the Environment
- 4.1 1. Increase Recycling Efforts
- 4.2 2. Practice Minimalism
- 4.3 3. Embrace Composting
- 4.4 4. Support Secondhand Shopping
- 4.5 5. Engage in Community Initiatives
- 5 Conclusion
The demand for efficient energy storage solutions has grown exponentially in today’s fast-paced world. As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources and electric vehicles, the importance of energy-dense, clean, and sustainable power storage has become increasingly apparent. This is where lithium-ion batteries, with their remarkable capabilities, come into play. Not only do they provide a reliable energy storage solution, but they also contribute to environmental protection in several significant ways.
Threats of Traditional Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have been a staple of energy storage for decades due to their reliability and low cost. However, despite their widespread use, they pose significant threats to human health and the environment. Understanding these threats is essential for promoting the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy storage solutions.
Environmental Pollution:
Lead-acid batteries contain lead, a toxic heavy metal. Improper disposal or recycling of these batteries can result in lead leaching into the environment, contaminating soil and water sources. Additionally, the mining and smelting of lead for battery production contribute to air and water pollution, impacting ecosystems and posing serious health risks to wildlife and humans.
Health Risks:
Exposure to lead, whether through production, use, or disposal of lead-acid batteries, poses severe health risks. Lead poisoning can lead to neurological and developmental issues, especially in children, as well as cardiovascular and reproductive problems in adults. Workers involved in the manufacturing, recycling, and disposing of lead-acid batteries are particularly susceptible to lead exposure and its associated health hazards.
Inefficient Recycling:
While lead-acid batteries are recyclable, recycling poses environmental and health risks. Improper recycling practices, prevalent in some regions, can result in lead emissions and toxic waste. Furthermore, the recycling process may not capture all the lead, leading to potential contamination of recycled lead-acid battery products, perpetuating the cycle of pollution and health risks.
Limited Energy Density:
Lead-acid batteries have a lower energy density than newer technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries. This limitation makes them less efficient for applications requiring high energy storage capacity, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. As a result, the continued reliance on lead-acid batteries inhibits the adoption of cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions, hampering efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Shorter Lifespan:
Lead-acid batteries generally have a shorter lifespan than newer energy storage technologies, necessitating more frequent replacements. This increases the demand for new batteries and results in a greater volume of battery waste that must be managed, further exacerbating the environmental impact of lead-acid batteries.
Using traditional lead-acid batteries presents significant threats to the environment, human health, and sustainable development. Transitioning away from lead-acid batteries towards cleaner and more efficient energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and other advanced solutions, is crucial for reducing pollution, protecting human health, and fostering a more sustainable and innovative energy landscape.
Lithium Battery’s contribution to Environmental Protection
Before discussing the benefits of lithium deep-cycle batteries, let’s briefly understand lithium batteries.
What is a Lithium Deep Cycle Battery
A lithium deep cycle battery, or lithium-ion deep cycle battery, is a rechargeable battery explicitly designed for deep discharge cycles. These batteries are commonly used in applications that require sustained power delivery over extended periods, such as in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, marine applications, and off-grid power solutions.
The term “deep cycle” refers to the battery’s ability to undergo repeated deep discharges, where a significant portion of the battery’s capacity is used before recharging. This is in contrast to starting batteries, designed to deliver short bursts of high power to create an engine but are not intended for deep discharges.
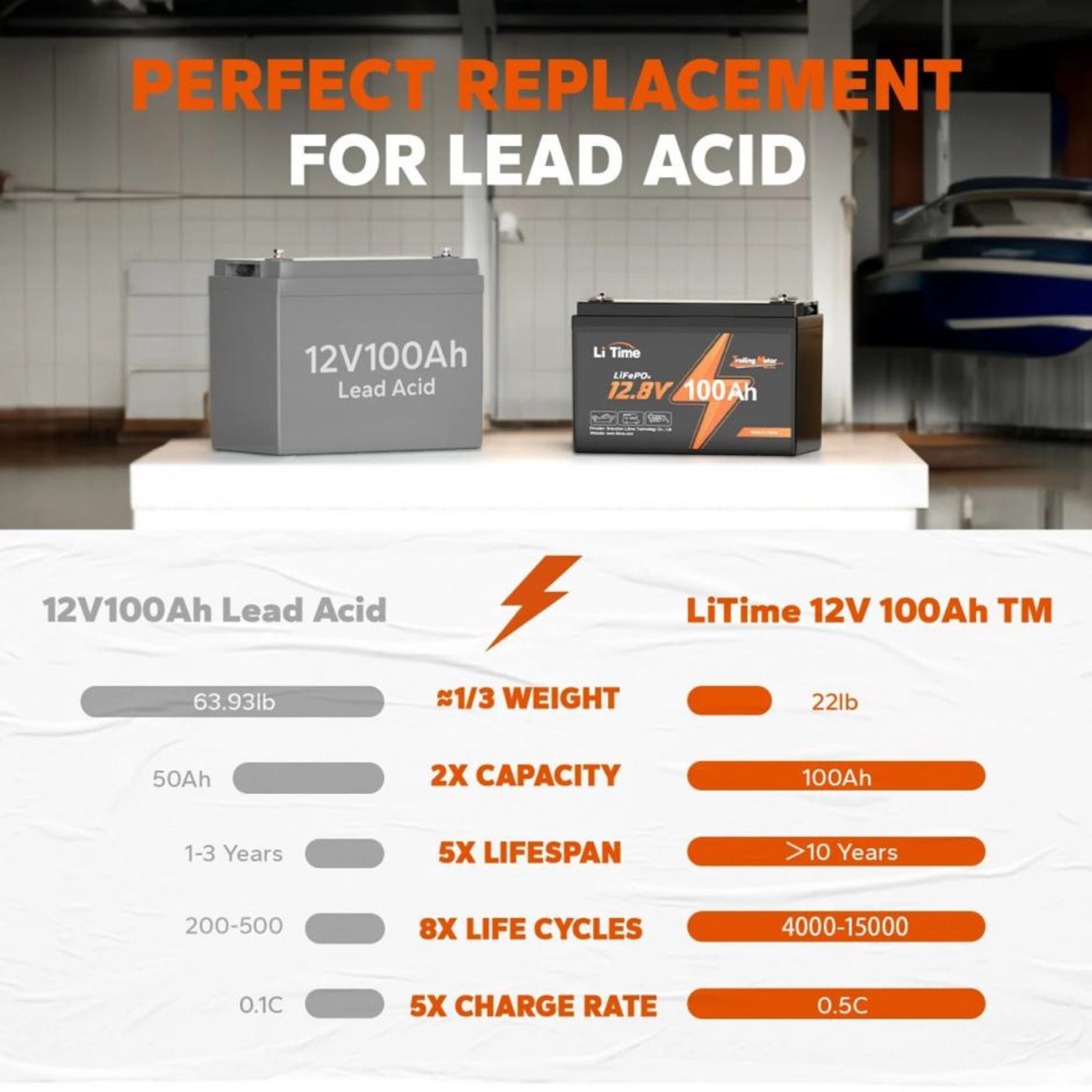
Lithium deep-cycle batteries offer several advantages over traditional lead-acid deep-cycle batteries, including:
High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries provide a higher energy density than lead-acid batteries, allowing more power to be stored in a smaller and lighter package.
Longer Cycle Life: Lithium deep-cycle batteries typically have a longer cycle life than lead-acid batteries, meaning they can withstand a greater number of charge-discharge cycles before experiencing a significant decrease in performance.
Fast Charging: Lithium-ion batteries can be charged faster than lead-acid batteries, allowing quicker recharge and enhanced energy availability.
Lighter Weight: Lithium deep cycle batteries are more lightweight than lead-acid batteries and have similar energy storage capacity, making them advantageous in applications where weight is critical.
Maintenance-Free Operation: Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion deep-cycle batteries do not require regular maintenance, such as topping up with water or equalizing charges.
How Lithium Deep Cycle Batteries Protect the Environment
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Lithium-ion batteries play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By enabling the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage, these batteries help decrease the reliance on fossil fuels. As a result, they contribute to lowering carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions, thereby mitigating climate change and its associated environmental impacts.
Efficient Energy Storage:
One of the primary benefits of lithium-ion batteries is their high energy density and efficiency. This enables the storage of renewable energy generated from solar and wind power sources. By storing excess energy and releasing it when needed, these batteries enhance the stability and reliability of renewable energy systems, thereby promoting the transition to cleaner energy sources.
Extended Product Lifespan:
Lithium-ion batteries generally have a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries, requiring more frequent replacements. For instance, LiTime lithium batteries boast a life cycle of over 4000 cycles, equating to a service lifespan of over ten years. This lifespan is three times longer than traditional lead-acid batteries, typically lasting only 3-5 years.
This longevity reduces the number of batteries that must be manufactured and disposed of, thereby decreasing the environmental impact of battery production and waste management.
Minimal Environmental Impact:
Lithium-ion batteries have a relatively lower environmental impact than conventional battery technologies. They contain fewer toxic materials, such as lead and cadmium, making them easier to recycle. Additionally, advancements in battery recycling technologies are making it increasingly feasible to recover and reuse valuable materials, further reducing the environmental footprint of lithium-ion batteries.
Driving Sustainable Practices:
The widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries promotes sustainable practices across various industries, particularly in the transportation and energy sectors. Lithium-ion batteries are instrumental in driving the global transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future by encouraging the development and use of clean and efficient technologies.
Promoting Circular Economy Principles:
Lithium-ion batteries are at the forefront of the transition towards a circular economy, where products and materials are reused, repaired, and recycled to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. By supporting the development of closed-loop systems for battery recycling and reuse, the industry is actively working towards reducing its environmental impact and conserving valuable resources.
The widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries is instrumental in advancing environmental protection efforts and promoting sustainable practices across various industries. As technology continues to evolve, further research and development in battery technology and recycling processes will continue to enhance the positive environmental impact of lithium batteries, reinforcing their crucial role in achieving a more sustainable future for the planet.
Additional Ways to Support the Environment
1. Increase Recycling Efforts
Reducing the amount of disposed items and increasing recycling efforts significantly contributes to environmental welfare. This includes not only conventional materials like soda bottles, soup cans, and newspapers but also electronics and items with scrap metal content, which carry hazardous toxins that can adversely affect landfill soil and water. Despite 75 per cent of waste being recyclable, only 30 per cent is recycled. Understanding the impact of recycling on the environment is crucial.
2. Practice Minimalism
The less we accumulate, the less we need to dispose of in the future. For instance, if you enjoy reading, downloading books onto a tablet rather than getting physical copies can help reduce unnecessary waste. Research suggests that Americans generate approximately 4.3 pounds of trash per person each day, much of which could be minimized.
3. Embrace Composting
Americans discard roughly 40 per cent of the annual food supply, amounting to 1,160 pounds per person. Food waste is the leading component in landfills and a significant source of methane emissions. Composting is an effective way to divert organic materials from landfills, conserve energy, and create nutrient-rich soil for gardening. Many cities provide composting resources, and those with suitable outdoor space can engage in outdoor composting.
4. Support Secondhand Shopping
Purchasing secondhand items, including clothing, offers an environmentally conscious approach to reducing waste. Americans dispose of roughly 14 million pounds of clothing annually, highlighting the potential for recycling unwanted items through secondhand shopping and minimizing the issue known as “fast fashion waste.”
5. Engage in Community Initiatives
In today’s digital era, connecting with individuals who share environmental concerns is easier than ever. Forming local alliances with friends, neighbours, and coworkers can foster collaborations on community-based efforts. Engaging in such initiatives serves the environment and provides opportunities to expand social circles and networks.
These straightforward ideas are easy to adopt and can have a significant positive impact.
Conclusion
In summary, efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions have become vital in today’s fast-paced world. The rise of renewable energy sources and electric vehicles highlights the crucial role of lithium-ion batteries in meeting these demands and their significant contributions to environmental protection. On the other hand, the continued reliance on traditional lead-acid batteries poses severe threats to the environment and human health.
Transitioning to cleaner and more efficient energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, is essential for reducing pollution, safeguarding human health, and promoting a more sustainable energy landscape.
Together, the widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries and the conscientious efforts of individuals to support the environment through their daily choices are crucial steps toward achieving a more sustainable future for our planet.