CNC Machining vs 3D Printing: What are the Differences?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing and prototyping, two cutting-edge technologies have become more and more popular, each offering unique advantages and applications. CNC machining and 3D printing represent distinct approaches to turning ideas into reality, which help to meet various industry requirements.
However, as these technologies continue to change the way we bring ideas to life, understanding their differences is very helpful in choosing the right manufacturing process for your projects!
What is CNC machining?
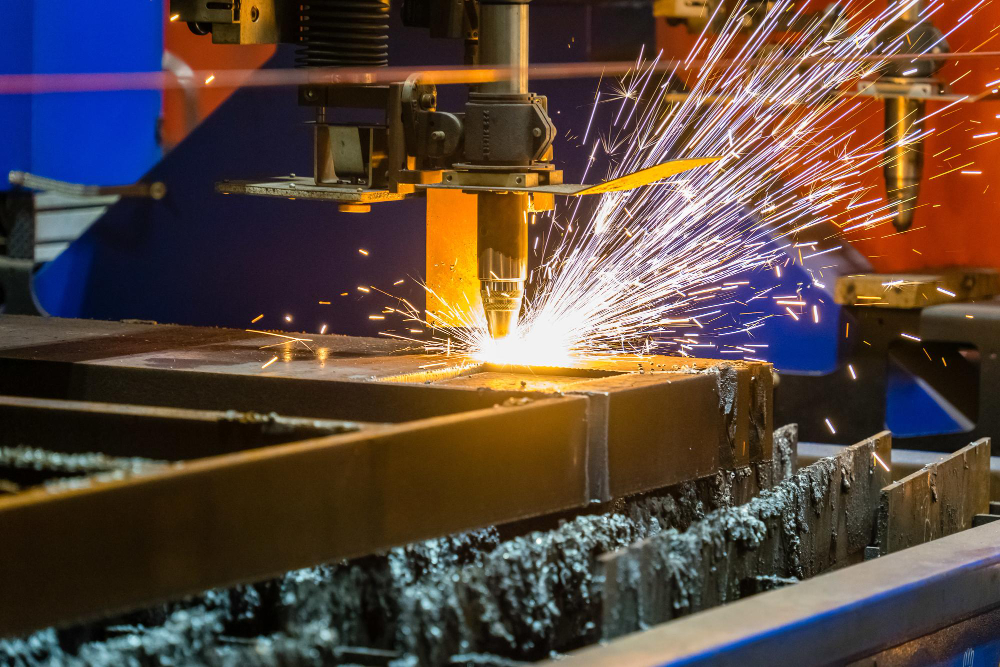

CNC machining (Computer Numerical Control Machining) is a common subtractive manufacturing process that produces shaped precision CNC machined parts by removing excess material from the original material using computer control and a series of complex machines, such as grinders, lathes, drill bits, plasma cutters, laser cutters, and milling machines.
This process includes CNC milling, CNC turning, CNC drilling, and other services. CNC processing has the advantages of stable processing quality, high processing accuracy, high repeatability, complex surface processing, and high processing efficiency. Typically, CNC equipment is used to manufacture parts that are durable, precise, and heat-resistant. CNC machining can be used in almost all industries, from small workshops to large production plants. This technology has a wide range of applications, including jewelry, hardware molds, castings, etc.
What is 3D Printing?
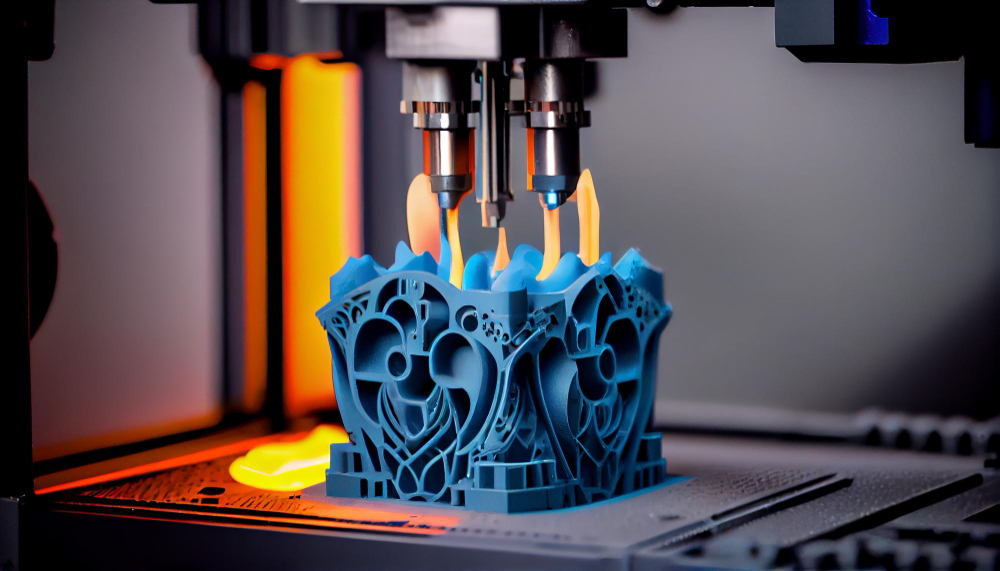

3D printing is a type of rapid prototyping technology that differs from CNC subtractive machining in that it is an additive manufacturing process. It is a digital manufacturing technology that directly molds complex structures in three dimensions by adding material layer by layer and constructs a 3D object from a computer-aided design (CAD) model.
3D printing includes Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), fused deposition molding (FDM), etc. 3D printing service has the advantages of low processing costs and short production cycles. It is used extensively in mechanical engineering, jewelry, aerospace, medical, and even in food printing, bioprinting, and construction.
Difference Between 3D Printing and CNC Machining
3D printing and CNC machining have some similarities and differences. Next will be mainly from the material, accuracy, processing speed, geometry, and post-processing five aspects of a comparative analysis of them.
Materials
The CNC machining process can work with a wide range of materials, mainly for metals, but also plastics, thermoplastics, acrylics, cork and hardwoods, molding foams, and waxes.
3D printing is relatively limited compared to CNC machining in terms of the materials it can work with, mainly plastics and to a lesser extent metals. Some technologies can produce parts from ceramics, waxes, and composites.3D printers are unable to use every material used by traditional manufacturers because the high melting point may deform the metal.
Common CNC Machining Materials
Plastics: ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, PEEK;
Metals: Aluminum, Stainless steel, Tanium, Brass.
Commonly 3D Printing Materials
Nylon, PLA, ABS, ULTEM, ASA, TPU, Resin.
Accuracy
Regardless of the material used, a CNC machine can produce high-precision parts with better tolerances than a 3D printer. Its positioning accuracy is very precise and the error is very small (depending on the geometry, the accuracy of CNC equipment is around 0.01mm – 0.05mm). Good manufacturers can provide products with 0.01mm accuracy. However, incorrect use can damage the tool and create defective parts. That’s why this job requires a well-trained professional operator.
Compared with CNC, the definition and surface quality of 3D printers are not good enough (3D printing layer thickness is around 0.1mm – 0.5mm). This is more suitable for those products that do not have such high requirements for precision and surface treatment. Thus, the advantages of additive manufacturing outweigh the disadvantages.
Production Speed
CNC machining requires skilled preparation for tool selection and programming of tool paths. This can take quite some time before the first processing. However, cutting is often fast, and complex parts can often be completed in an hour or less of actual machining. Total preparation and processing time can take a day or more, depending on complexity. On the other hand, the print preparation of 3D components takes very little time before printing starts. Although printing is slow in some respects, most prints will likely be complete and ready to use within a few hours.
Geometry
Certain geometries cannot be CNC machined due to the limitations of the CNC when designing the part. 3D printing has few geometric limitations compared to CNC. With 3D printing, hollow, complex geometries can be completed. Combining these two fabrication techniques enables new design solutions. The combination of subtractive and additive manufacturing can further advance the advancement and development of designs.
Post-processing
There are many post-processing options for CNC-processed parts, such as oil injection, grinding, deburring, silk screen printing, electroplating, pad printing, laser engraving, oxidation and sandblasting, etc.
The post-processing of 3D printed parts is much simpler than that of CNC, generally including grinding, deburring, oil injection, and dyeing.
Conclusion
CNC machining and 3D printing are both versatile technologies. They are therefore used in a variety of applications including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products. Every project must consider the combination of material characteristics, precision, speed, and cost mentioned above. In some cases, the best approach is to combine CNC machining and 3D printing to create a part that meets all functional and aesthetic requirements.