An Overview of Optical Interconnect Technology
- 1 What is Optical Interconnect Technology?
- 2 Advantages of Optical Interconnect Technology
- 2.1 High-Speed Data Transfer:
- 2.2 Low Latency:
- 2.3 Long Distance Transmission:
- 2.4 Low Power Consumption:
- 3 Applications of Optical Interconnect Technology
- 3.1 Data Centers –
- 3.2 Telecommunication Networks –
- 3.3 High-Performance Computing Systems –
- 3.4 Military Applications –
- 4 What Does the Future Hold?
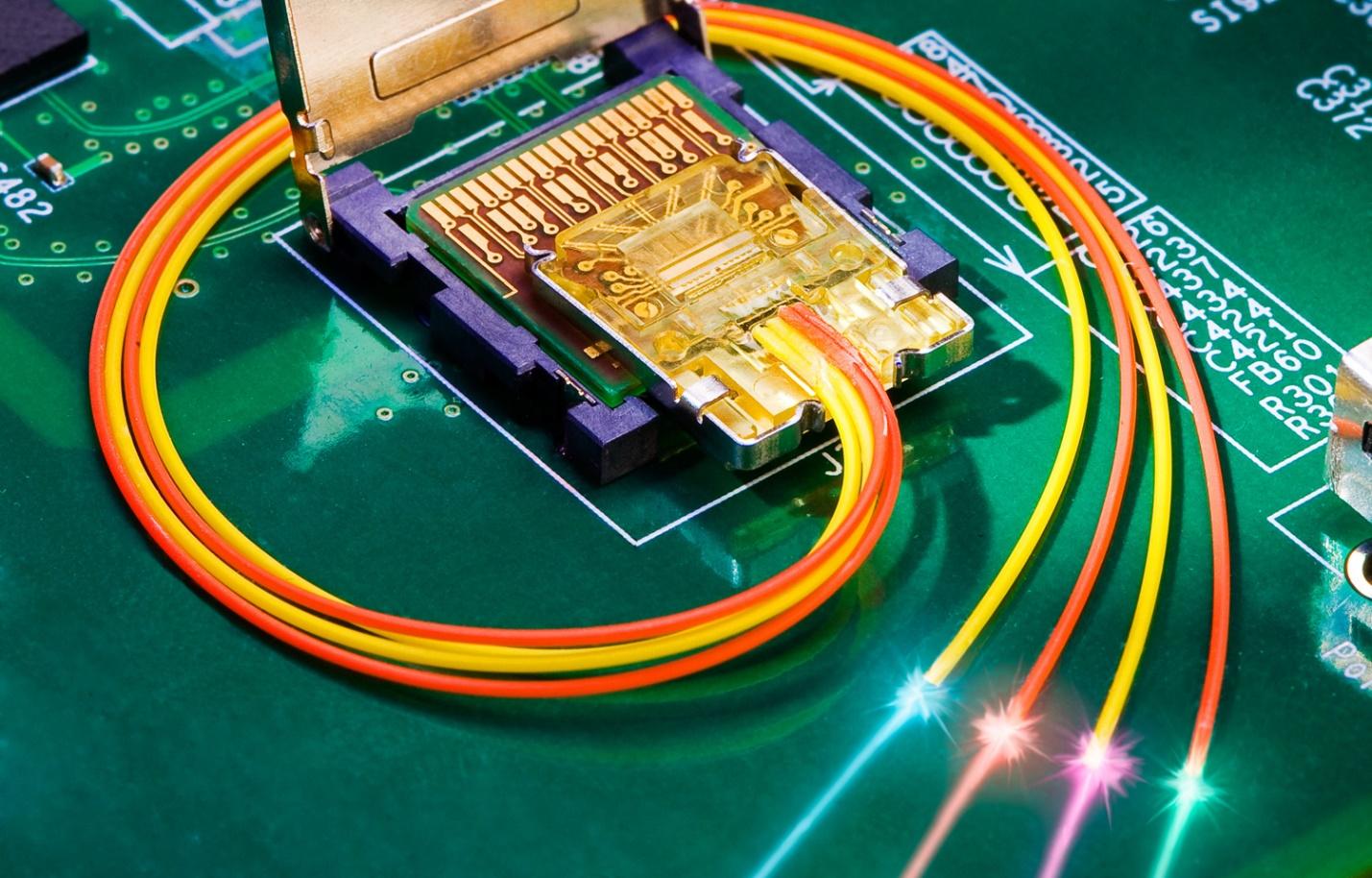
In today’s fast-paced world, the need for faster and more efficient data transmission has become more critical than ever before. The increasing demand for high-speed data transfer, particularly in data centres and cloud computing, has made optical interconnect technology attractive.
Optical interconnects use optical fibre cables to transmit data at the speed of light, enabling faster and more efficient data transfer. This blog will provide an overview of optical interconnect technology, its advantages, and its applications.
What is Optical Interconnect Technology?
Optical interconnect technology is a method of transmitting data through optical fibre cables. Unlike traditional copper wires, which transmit data using electrical signals, optical fibres use light signals to transfer data. Optical interconnect technology is used in various applications, including data centres, telecommunication networks, and high-performance computing systems. It has become increasingly popular due to its high-speed data transfer capabilities, low latency, and low power consumption.
Advantages of Optical Interconnect Technology
There are several advantages of using optical interconnect technology, including:
High-Speed Data Transfer:
Optical interconnects can transmit data at up to 100 Gbps, significantly faster than traditional copper wires.
Low Latency:
Optical interconnects have low latency, meaning data can be transmitted quickly and efficiently without delay.
Long Distance Transmission:
Optical fibres can transmit data over long distances without signal degradation, making them ideal for long-distance data transfer.
Low Power Consumption:
Optical interconnects use less power than traditional copper wires, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
Applications of Optical Interconnect Technology
Optical interconnect technology has numerous applications, including:
Data Centers –
Data centres widely use optical interconnects to connect servers, storage systems, and switches. They enable faster and more efficient data transfer between these devices, improving overall system performance.
Telecommunication Networks –
Optical interconnects are used in telecommunication networks to connect different network nodes, such as base stations and central offices. They provide high-speed data transfer, enabling faster and more efficient communication between these nodes.
High-Performance Computing Systems –
Optical interconnects are used in high-performance computing systems, such as supercomputers, to connect different computing nodes. They enable faster data transfer between these nodes, improving overall system performance.
Military Applications –
Optical interconnects are also used in military applications, such as aircraft and submarines, to transmit data securely and efficiently.
What Does the Future Hold?
Optical interconnect technology’s future looks promising as it offers numerous advantages over traditional electrical interconnects. Optical interconnect technology uses light waves to transmit data, which enables it to provide high-speed data transfer rates and lower power consumption.
One of the critical trends in optical interconnect technology is the move towards silicon photonics. This technology involves integrating photonic devices, such as lasers and modulators, directly onto silicon chips, which enables the creation of low-cost, high-performance optical interconnects. Silicon photonics is expected to play a significant role in developing future data centres and high-performance computing systems.
Another trend is the development of plasmonic interconnects. Plasmonics uses surface plasmon polaritons, oscillations of electrons on the surface of metals, to transmit data. Plasmonic interconnects have the potential to offer even higher speeds and greater bandwidth than traditional optical interconnects.
There is also a growing interest in the use of quantum dot-based interconnects. Quantum dots are tiny semiconductor particles that can emit light of a specific colour when excited by a laser. Quantum dot-based interconnects have the potential to offer high-speed data transfer rates, low power consumption, and compatibility with existing CMOS technology.
In conclusion, the future of optical interconnect technology looks very bright, with silicon photonics, plasmonic interconnects, and quantum dot-based interconnects all showing great promise. As data rates continue to increase and power consumption becomes an increasingly important consideration, optical interconnects are likely to become even more prevalent in future computing systems.