What Is the Link Between PCOS and Irregular Menstrual Cycles?
- 1 What is PCOS?
- 2 What Are Irregular Menstrual Cycles?
- 3 How Does PCOS Influence the Menstrual Cycle?
- 3.1 1. Hormonal Imbalance
- 3.2 2. Insulin Resistance
- 3.3 3. Lack of Ovulation (Anovulation)
- 3.4 4. Endometrial Overgrowth
- 4 Signs That PCOS May Be Affecting Your Period
- 5 Managing Irregular Periods Caused by PCOS
- 5.1 1. Medications for Controlling Periods
- 5.2 2. Lifestyle Modifications
- 5.3 3. Birth Control Pills
- 5.4 4. Fertility Treatments
- 5.5 5. Monitoring and Follow-up
- 6 Why Treating Irregular Periods Matters
- 7 Takeaway
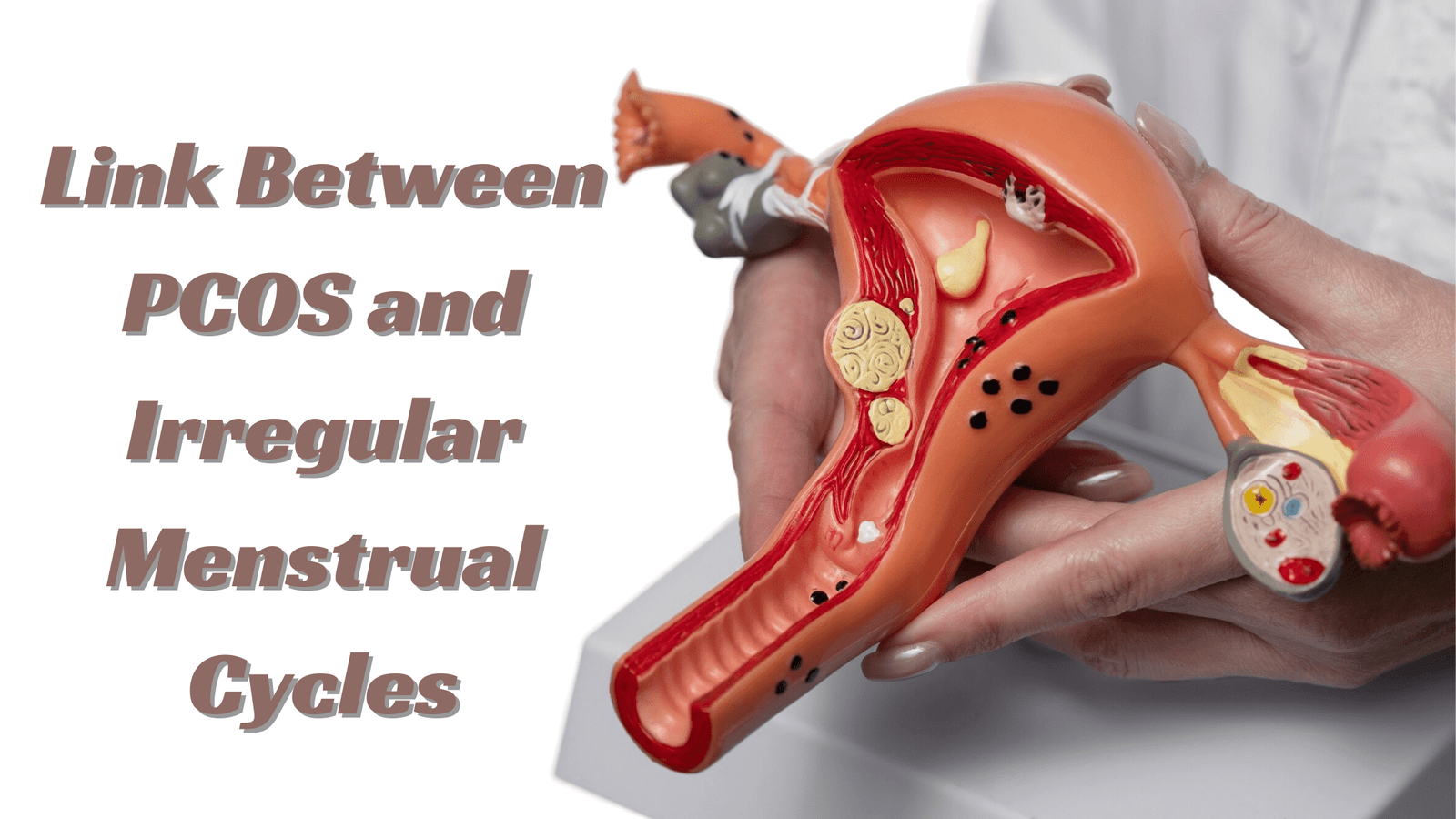
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age. Irregular menstrual cycles are one of the classic signs of PCOS. PCOS can go unnoticed in many women until their periods, fertility, or other health problems become a problem. The connection between PCOS and irregular periods is rooted in how this syndrome interferes with the hormonal balance necessary for regular ovulation and menstruation.
In this article, we’ll explore what PCOS is, how it causes irregular periods, and how it can be managed with medications, lifestyle changes, and medical supervision.
What is PCOS?
PCOS, short for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a hormonal disorder that influences the ovaries and ovulation. In PCOS, the ovaries can have many small cysts (fluid-filled pouches) and be unable to release eggs regularly. This results in a chain effect in the body’s hormone levels, impacting menstrual frequency, skin, weight, and even fertility.
Based on doctors, PCOS strikes approximately 1 in 10 women worldwide. Yet many remain undiagnosed as the symptoms may be different and sometimes confused with other illnesses or tension.
What Are Irregular Menstrual Cycles?
The normal menstrual cycle is 21 to 35 days long. An abnormal cycle is when the time between periods is quite different from month to month, or sometimes bleeding may completely cease for a couple of months. A few women have very heavy or extended bleeding, and others have light or irregular periods.
In PCOS, irregular periods are more than a mere nuisance—they are a signal that ovulation is not happening as it should be. Managing this condition may involve hormonal support through medicines, including dydrogesterone tablets, to help restore regular menstrual function.
How Does PCOS Influence the Menstrual Cycle?
PCOS influences menstrual cycles in a few different ways:
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Women with PCOS tend to have higher amounts of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone. These excess androgens disrupt the growth of the ovarian follicles, the tiny sacs that contain and release eggs. If the follicles don’t grow properly, ovulation won’t take place, causing infrequent or absent periods.
2. Insulin Resistance
Most women with PCOS also have insulin resistance, whereby their bodies fail to respond well to insulin. This can result in elevated levels of insulin in the body, which can then activate the ovaries to produce excess androgens. This creates a cycle that interferes with ovulation and menstruation.
3. Lack of Ovulation (Anovulation)
Ovulation is needed for normal periods. When ovulation doesn’t happen (a state called anovulation), the lining of the uterus won’t shed normally, resulting in irregular or missing periods.
4. Endometrial Overgrowth
When periods are delayed or missed, the lining of the uterus keeps thickening. Later, when a period does happen, it can be heavier and more painful than normal.
Signs That PCOS May Be Affecting Your Period
If you are having one or more of the following symptoms, it can be a sign of PCOS-related menstrual irregularity:
- Periods fewer than 8 times per year
- Gaps longer than 35 days between periods
- Very heavy or very light periods
- Having trouble knowing when your next period will come
- Spotting in between periods
- Fertility problems or pregnancy difficulties
The good news is that PCOS-induced irregular periods can be controlled with proper medical treatment and lifestyle modifications. The treatment varies based on the degree of symptoms and whether the woman wants to become pregnant.
Managing Irregular Periods Caused by PCOS
1. Medications for Controlling Periods
Dydroboon Tablet
The Dydroboon Tablet is an ingredient that comprises dydrogesterone, a man-made hormone that is analogous to the natural progesterone that the body naturally produces. The medicine can restore hormonal balance and normalise menstrual cycles in women with PCOS. It achieves this by simulating the action of progesterone, which triggers a normal period.
This medicine is particularly beneficial for women who do not ovulate on a regular basis since it helps in the development and shedding of the uterine lining.
Dydrocare 10 Tablet
Dydrocare 10 Tablet also has dydrogesterone and is widely prescribed to regularize periods in women with hormonal imbalance caused by PCOS. It is safe, well-tolerated, and may also be prescribed to women who are seeking conception under medical supervision.
These medications are typically taken for a certain number of days each month based on the individual’s hormone profile and advice from the doctor.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medications, lifestyle modifications can also improve PCOS symptoms as well as manage periods.
- Weight Management: Reducing weight by 5–10% can restore ovulation and regular periods.
- Balanced Diet: A diet with whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein helps manage insulin and hormonal balance.
- Exercise: Daily exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes weight loss.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalance. Activities such as yoga, meditation, or merely regular hobbies may be helpful.
3. Birth Control Pills
Hormonal birth control pills are typically used in non-pregnant women who do not want to become pregnant to control the menstrual cycle, decrease levels of androgen, and manage symptoms such as acne and hirsutism.
4. Fertility Treatments
For women with PCOS wishing to conceive, ovulation-stimulating medications like clomiphene citrate, letrozole, or gonadotropins can be advised. In certain situations, assisted reproductive technology like IVF can become essential.
5. Monitoring and Follow-up
Periodic visits to a gynaecologist or endocrinologist are crucial in treating PCOS and its complications. Blood tests, ultrasound scans, and monitoring of symptoms assist doctors in customizing treatment plans accordingly.
Why Treating Irregular Periods Matters
Untreated irregular periods in PCOS have long-term effects, including:
- Infertility
- Risk of endometrial hyperplasia or cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Depression and anxiety
Early diagnosis and regular management of PCOS are therefore important for long-term reproductive and overall health.
Takeaway
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a multifaceted disorder that has a major impact on the menstrual cycle. The connection between PCOS and irregular periods is in the hormonal disorders that cause disrupted ovulation, resulting in irregular or missing menstruation. Recognizing such patterns can enable women to initiate medical help in good time.
Coupled with lifestyle changes and medication monitoring, women with PCOS can successfully control the condition and live healthy, productive lives.
If you have a suspicion of PCOS or irregular periods, it is necessary to consult a medical practitioner. Early treatment and diagnosis can avoid complications and aid reproductive health.