Plastic Injection Moulding: The Basics
Plastic injection molding stands as one of the most versatile and widely used manufacturing processes in the world. It revolutionized the way products are designed, prototyped, and mass-produced. From intricate components in electronics to everyday consumer goods, the impact of plastic injection molding is ubiquitous. This article delves into the depths of this fascinating process, exploring its innovation, sustainability efforts, and future trends.
Understanding Plastic Injection Moulding:
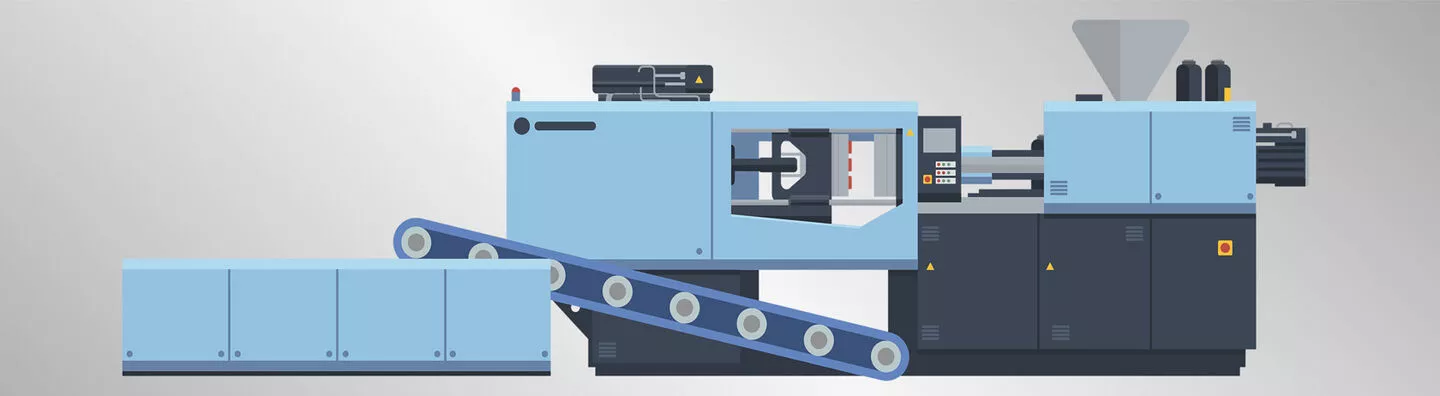
At its core, plastic injection molding involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity, where it solidifies to form the desired shape. The process typically begins with the design of the mold, followed by the selection of suitable plastic resins. These resins, often in pellet form, are heated and injected under high pressure into the mold, where they cool and solidify, taking the shape of the mold cavity.
Innovation in Plastic Injection Moulding:
Advanced Materials:
The evolution of plastic materials has been instrumental in driving innovation in injection molding. High-performance polymers, bioplastics, and composite materials offer enhanced properties such as strength, durability, and heat resistance, opening up new possibilities for product design.
Precision Engineering:
Advancements in mold-making technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer numerical control (CNC) machining, and 3D printing, have enabled the creation of intricate molds with high precision and repeatability. This allows for the production of complex geometries and fine details in finished parts.
Automation and Robotics:
Automation has transformed the efficiency and scalability of plastic injection molding operations. Automated systems handle tasks such as material feeding, molding, and part ejection, reducing cycle times and minimizing human intervention. Robotics further optimize production processes, enabling functions like part inspection, assembly, and packaging to be performed with speed and accuracy.
Sustainability in Plastic Injection Moulding:
Material Recycling:
The plastics industry has been increasingly focused on improving recycling rates and reducing plastic waste. Injection molding facilitates the use of recycled plastic materials, helping to close the loop on plastic waste streams. Recycled resins can be used in combination with virgin materials or processed into new products, reducing the demand for raw materials and mitigating environmental impact.
Eco-Friendly Materials:
The development of bio-based and biodegradable plastics offers a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based polymers. These materials are derived from renewable sources such as plant biomass and degrade naturally, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing pollution.
Energy Efficiency:
Energy consumption is a significant consideration in injection molding operations. Manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient equipment, optimizing process parameters, and implementing waste heat recovery systems to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Future Trends in Plastic Injection Moulding:
Additive Manufacturing Integration:
The integration of additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, with traditional injection molding processes is poised to revolutionize product development and customization. Hybrid systems enable the rapid prototyping of mold inserts and the production of customized components with minimal tooling costs.
Smart Manufacturing:
The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles in injection molding facilities is driving the development of intelligent, connected manufacturing systems. Sensor-enabled machines, real-time monitoring, and data analytics optimize process efficiency, predict maintenance needs, and enable remote management of production operations.
Sustainable Design:
The emphasis on sustainable design principles is reshaping product development strategies in the plastics industry. Design for recycling, biodegradability, and circularity are becoming integral considerations in the design process, driving the demand for eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion:
Plastic injection molding continues to evolve in response to technological advancements, market demands, and sustainability imperatives. From innovation in materials and processes to the embrace of sustainable practices, the future of injection molding holds promise for greater efficiency, flexibility, and environmental responsibility. As manufacturers embrace new technologies and design philosophies, plastic injection molding will remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, shaping the products of tomorrow.