Advantages of GDPR Compliance
- 1 Seven Principles of GDPR
- 1.1 Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
- 1.2 Purpose limitation
- 1.3 Data Minimization
- 1.4 Accuracy
- 1.5 Storage limitation
- 1.6 Integrity and confidentiality
- 1.7 Accountability
- 2 Eight fundamental rights of GDPR
- 2.1 Access:
- 2.2 Forgotten:
- 2.3 Portability:
- 2.4 Processing:
- 2.5 Correction:
- 2.6 Information:
- 2.7 Object:
- 2.8 Notified:
- 3 Importance of GDPR compliance for your business
- 3.1 Conclusion
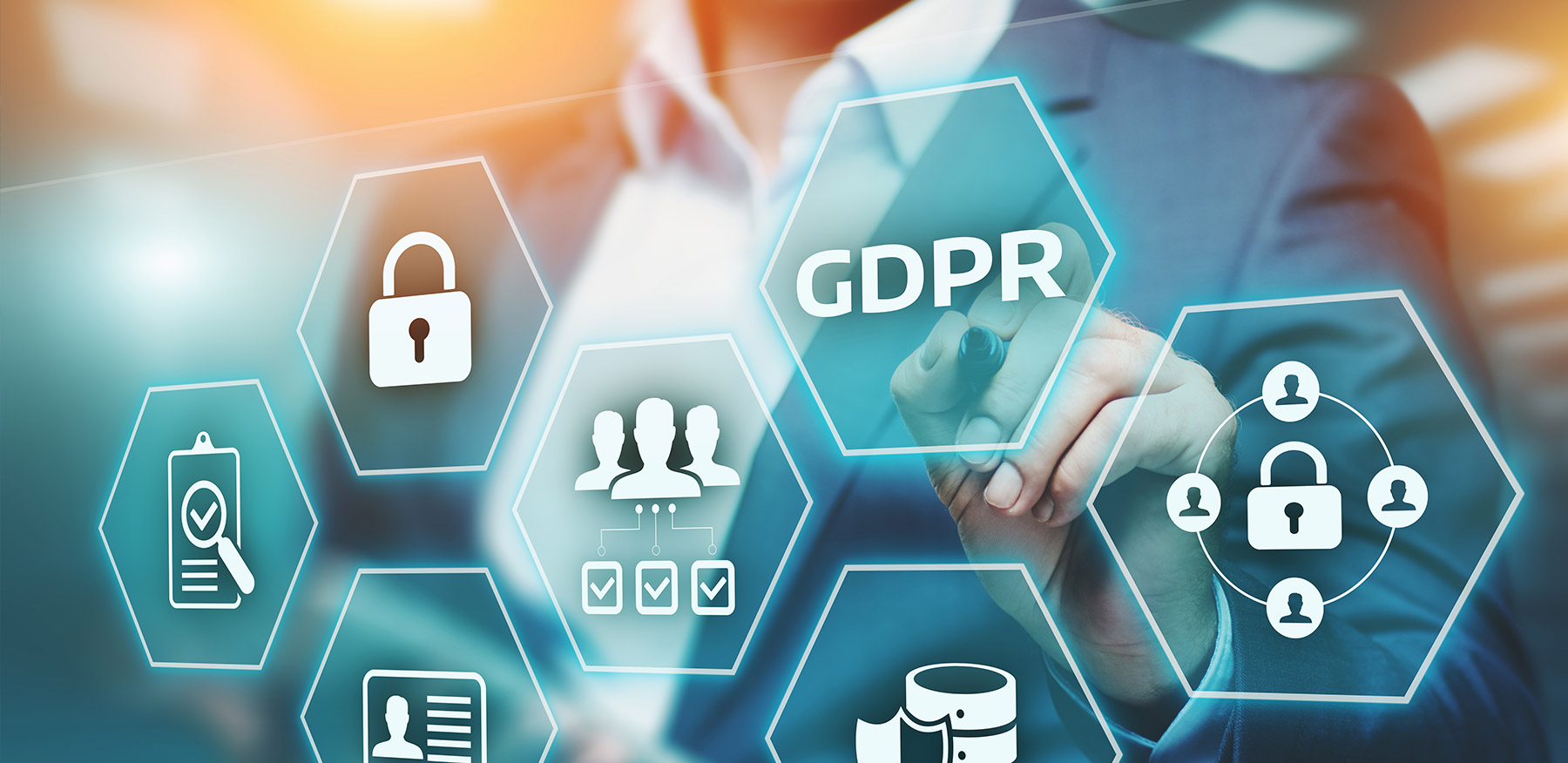
The General Data Protection Regulation, GDPR, is a rule imposed for all businesses in the EU that govern organizational privacy and personal data protection. The GDPR is looked upon as one of the strictest regulations in terms of data collection, privacy, and security. It is obvious that personal data is very sensitive, and there must be strict laws surrounding it so that the data for individuals remain safe and secure.
All businesses, especially those in the European Union, are strictly subjected to comply with the GPDR regulations. Although assuring you compliance with GDPR can be a hefty and tough challenge, there are indeed many benefits that GDPR compliance can bring to your business. In this blog, we will explain to you GDPR and what advantages it provides to your firm.
Seven Principles of GDPR
Before going any further ahead, it is important to be updated on the seven principles of GDPR. The seven principles are as follows:
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
The first GDPR principle utilises words with distinct meanings. Three factors are in place: lawfulness, fairness, and transparency.
According to the definition of “lawfulness,” a company should only collect personal data with the user’s consent. The most acceptable and legal method of data collection is to obtain the client’s consent. Consent can be given either verbal form or in writing form by the users.
Fairness refers to how the organisation collects and uses the user’s data. A legitimate interest involves using the data for legal purposes, such as gathering customer preferences through an organisation.
Transparency refers to the company being open about how, what, and why it processes data.
According to this rule, all data must be legally processed and obtained with the user’s consent. The specific information on how data is being collected, its storing process, and how long it will stay in the business’s system must all be known to the data subject.
Purpose limitation
The data collected by the organisation must only be used for the intended purpose. The use must serve a specific and legal purpose. The controller cannot collect or process data in an illogical manner. If the company were found using the data for a purpose other than what was clearly stated, it would be considered GDPR noncompliance.
Data Minimization
The practice of corporations not maintaining extra data in their systems is known as data reduction. This indicates that businesses should erase data also while notifying their users that their data is no longer being processed. Many businesses save unnecessary data and never use it. As a result, firms should only gather exact and minimal data for their processing. This would be a breach of the GDPR.
Accuracy
Companies should only collect correct data from the users. Procedures should be in place to guarantee that all erroneous data is updated or destroyed as soon as possible.
Storage limitation
This GDPR principle requires the organisation to erase all personal data after processing. Personal information about a company’s users that is no longer required should not be kept. Customers must also be told how long the organisation collects their data and intends to keep it. It also ensures that data is erased after it has been used.
Integrity and confidentiality
This GDPR principle emphasises the need for integrity and confidentiality. Only those with authority should have access to the data in order to guarantee data security and confidentiality. This increases customer and business trust while preventing unnecessary data loss. Integrity refers to acquiring data as precisely and sparingly as possible and safeguarding it against threats such as hacking.
Accountability
Accountability is the seventh and final GDPR principle. Accountability means that a corporation accepts full responsibility for the data it processes while adhering to all legal standards. The company should also be able to provide proof that these regulations were followed. Documentation can be used as evidence. GDPR regulators are aware that a corporation can assert verbally that it is complying with GDPR while not actually doing so. Because of this, a certain level of accountability is required.
Eight fundamental rights of GDPR
Under GDPR, users have the right to:
Access:
Users have the right to access their personal information from the organisation that has collected it. Additionally, the users have the right to find out how their data will be processed and what purpose it will serve for the organisation. Similarly, the business is responsible for providing all the information requested.
Forgotten:
The users can request the company delete all of their data if the customer is no longer a member of their company or if he feels like revoking their consent. In response, the company is required to obey the commands of the user.
Portability:
Users have the choice to ask for data transfer between service providers.
Processing:
The user can wish to stop the processing of their data whenever they want. In this matter, the organisation should stop the processing at all costs.
Correction:
Users have the option to add or remove any content from their data anytime they want.
Information:
The users have the right to know where their data is stored at the moment.
Object:
Users have the flexibility to edit any information in their records anytime they want.
Notified:
The users have the right to be informed as soon as possible if their data has been successfully processed by the organisation.
Importance of GDPR compliance for your business
GDPR is a set of standards that requires businesses to protect their consumers’ privacy and personal information. Given the growing concerns about data gathering and security, compliance with GDPR is more important than ever. GDPR training for employees is crucial to ensure that they are aware of the regulations and equipped with the necessary knowledge to handle personal data appropriately. This training helps employees understand their responsibilities, learn best practices for data protection, and minimize the risk of data breaches.
GDPR has the following commercial benefits for businesses:
- Legal compliance: Employers can save their businesses from legal actions by complying with GDPR regulations. These legal actions can be in the face of fines, sanctions and penalties.
- Protecting customer data: GDPR assists businesses in protecting their client’s privacy by ensuring that data is acquired and processed in a lawful, open, and secure manner. By protecting its data, a firm can avoid data breaches and cyberattacks, which can result in financial loss and reputational damage.
- Building customer trust: Compliance with GDPR can assist a firm in building a strong customer base with trust. Customers tend to respect and give attention to those organisations that are open and honest about their data processing activities and safety.
- Good data management practices: GDPR encourages businesses to implement acceptable data management processes such as access limits, data encryption, and frequent data backups. These practices help firms protect client data and prevent data breaches.
- Risk management: GDPR requires businesses to do risk assessments and implement the required security measures to protect data. These practices reduce the chance of data breaches and cyberattacks by assisting organisations in identifying and mitigating potential dangers to their customers’ data.
Conclusion
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a critical weapon for safeguarding people’s privacy rights. In many countries, GDPR compliance is required by law since data protection is a critical concern. This document thoroughly explains the eight essential rights of a data subject and the seven GDPR guiding principles.
Furthermore, this article has highlighted the procedures and importance of GDPR compliance for those firms. GDPR compliance provides a competitive advantage, protects consumer data, encourages trust and reputation, and aids in the avoidance of legal penalties. Companies can demonstrate their dedication to protecting their customers’ privacy by complying with GDPR.