Streamlining Content Creation Workflows With Automated Musical Composition Tools
- 1 Understanding The Mechanics Behind Text-Driven Audio Synthesis
- 1.1 From Semantic Prompts To Complex Melodic Arrangements
- 1.2 The Integration Of Lyrical Content Into Melodic Structures
- 1.3 Handling Syllabic Rhythm And Rhyme Schemes In Generation
- 2 Step-by-Step Workflow For Generating Custom Audio Tracks
- 2.1 Defining Musical Vision Through Descriptive Text Inputs
- 2.2 Processing Compositional Patterns And Audio Rendering
- 2.3 Exporting High Fidelity Audio For Commercial Application
- 2.4 Comparative Analysis Of Traditional Versus Algorithmic Production Methods
- 2.5 Assessing The Reliability And Quality Of Generated Audio Assets
- 2.6 Observations On Commercial Usability And Licensing Rights
- 2.7 Understanding Current Limitations In AI Musical Expression
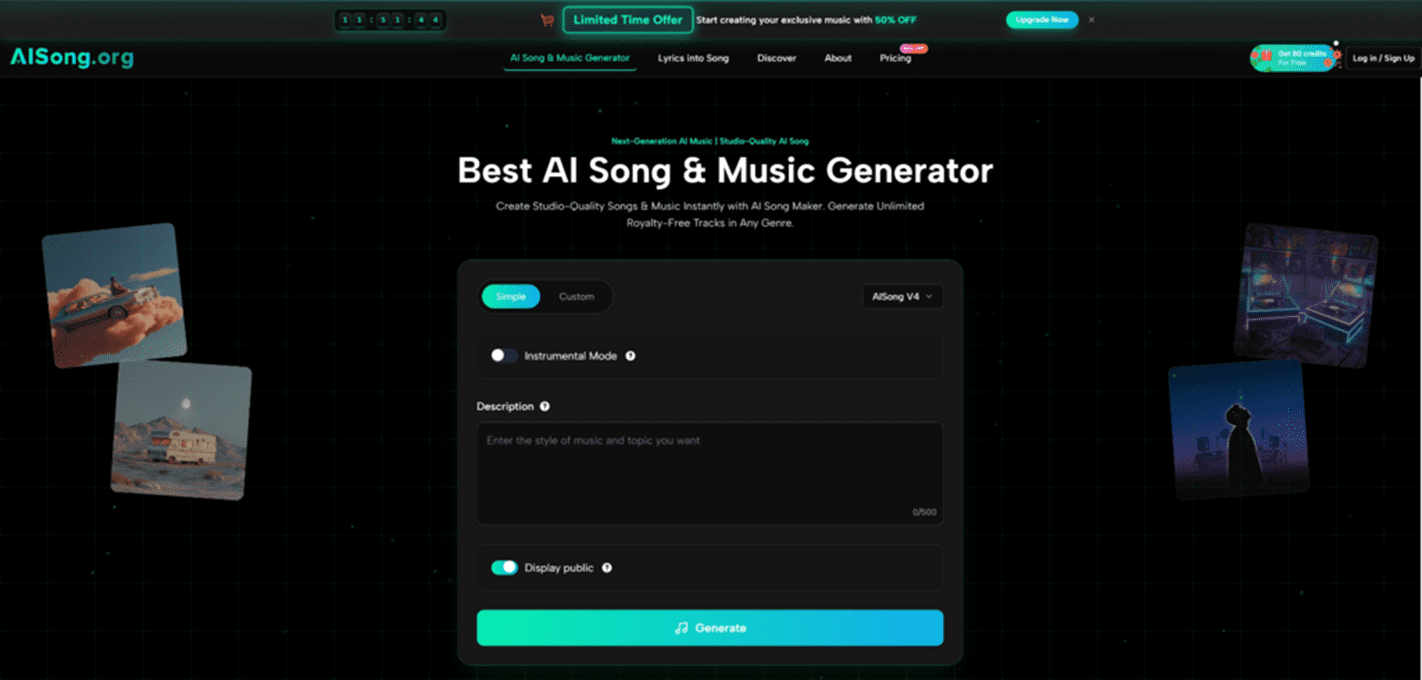
The modern digital landscape presents a persistent challenge for creators: sourcing high-quality, royalty-free audio that fits a specific narrative arc without incurring high costs or legal risks. Whether for a podcast intro, a video background, or a commercial presentation, the friction between budget constraints and copyright law often stifles creativity. This bottleneck has driven the development of the AI Song Generator, a tool designed to translate textual concepts into fully realized musical compositions. By leveraging advanced neural networks, this technology attempts to democratize music production, allowing users to bypass complex Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) and expensive licensing agreements in favor of a prompt-based generation model.
Understanding The Mechanics Behind Text-Driven Audio Synthesis
The core functionality of this platform relies on the interpretation of natural language inputs to dictate musical parameters. Unlike traditional loop libraries, where users must piece together pre-recorded stems, this system appears to synthesize audio from scratch based on semantic understanding. When a user inputs a descriptor such as “lo-fi hip hop for study sessions,” the underlying algorithms analyze the request to determine appropriate tempo, instrumentation, and harmonic structure.
From Semantic Prompts To Complex Melodic Arrangements
In my observation of the tool’s capabilities, the generation engine does not merely retrieve existing files but constructs new audio data. This distinction is crucial for content creators concerned with uniqueness. The system seems to break down the user’s prompt into key musical components—genre, mood, and instrumentation—and reassembles them into a coherent track. This process suggests a move away from rigid template-based creation toward a more fluid, generative approach where the output is theoretically unique to the specific combination of descriptors provided.
The Integration Of Lyrical Content Into Melodic Structures
A significant differentiation point for this platform is its ability to handle vocal synthesis. Users are not limited to instrumental tracks; the system allows for the input of custom lyrics. This feature suggests that the AI is capable of aligning syllabic rhythm with generated melodies, a complex task that typically requires human intuition. While the emotional delivery of AI vocals is an evolving field, the technical capability to match text to pitch and rhythm offers a rapid prototyping tool for songwriters and advertisers looking to test lyrical concepts before committing to a studio recording.
Handling Syllabic Rhythm And Rhyme Schemes In Generation
The engine appears to analyze the structure of input lyrics to determine verse-chorus patterns. In testing various lyrical inputs, one can observe that the system attempts to maintain a consistent meter, adjusting the melody to fit the length of the lines. This functionality is particularly relevant for users who need to produce jingles or narrative songs where specific messaging must be audible and rhythmically consistent with the backing track.
Step-by-Step Workflow For Generating Custom Audio Tracks
The user interface is designed to minimize the technical barrier to entry, reducing the music production process to a few intuitive actions. Based on the official workflow outlined on the platform, the creation process follows a linear path.
Defining Musical Vision Through Descriptive Text Inputs
The first step requires the user to articulate their creative intent. This involves typing a description into the input field that covers the desired style, mood, and genre. The platform is built to understand a wide range of descriptors, from specific genres like “upbeat pop” to atmospheric conditions like “melancholic jazz for rainy days.” For users with specific lyrical requirements, this stage also involves inputting the text that the AI will sing, effectively setting the thematic groundwork for the entire composition.
Processing Compositional Patterns And Audio Rendering
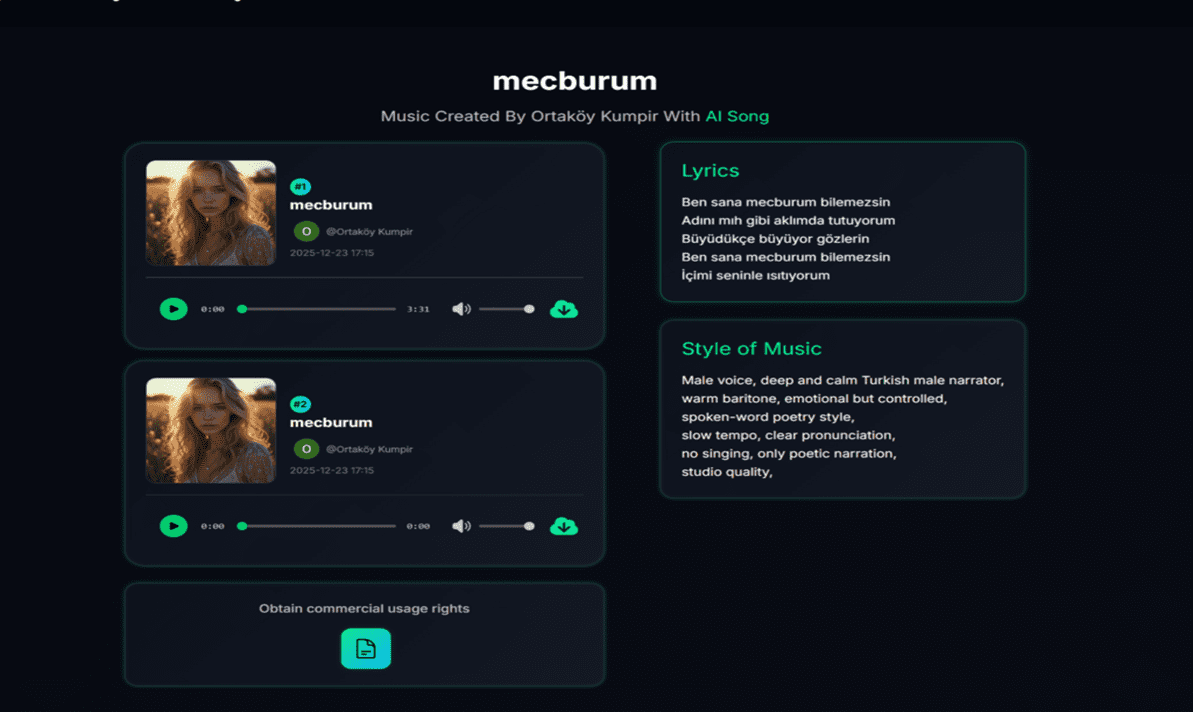
Once the description is submitted, the second phase involves the computational generation of the track. The system processes the input data, mapping the semantic requirements to musical theory rules. During this phase, the AI analyzes patterns to create original melodies, harmonies, and rhythms that align with the user’s specifications. This automated composition process eliminates the need for manual arranging or mixing, as the system handles the balancing of instruments and vocal levels internally.
Exporting High Fidelity Audio For Commercial Application
The final step in the workflow is the delivery of the asset. Upon completion of the generation process, the user is presented with the option to download the piece. The platform provides the audio in high-quality MP3 format, ensuring compatibility with most video editing software and media players. Crucially, the platform states that these downloads come with full commercial rights, allowing the generated music to be used in social media posts, videos, and other commercial projects without watermarks or attribution requirements.
Comparative Analysis Of Traditional Versus Algorithmic Production Methods
To understand the value proposition of this technology, it is helpful to contrast it with standard industry practices. The following table highlights the operational differences between hiring human composers or using stock libraries versus utilizing an AI-driven approach.
| Feature Category | Traditional Production / Stock Music | AI Music Generation Platform |
| Cost Efficiency | High costs for licensing or hiring session musicians | Significantly lower, often free for basic generation |
| Production Time | Days to weeks for custom composition; hours for searching stock | Minutes to generate a complete track |
| Customization | High manual control, but requires technical expertise | High conceptual control via text, low technical barrier |
| Copyright Status | Complex licensing tiers and potential royalty fees | Royalty-free with commercial usage rights included |
| Uniqueness | High uniqueness for custom; low for stock libraries | Theoretically unique generation per prompt |
| Skill Requirement | Requires knowledge of music theory and DAW software | Requires no musical training or technical skills |
Assessing The Reliability And Quality Of Generated Audio Assets
While the speed and accessibility of the tool are evident, the quality of the output remains a critical factor for professional adoption. The platform positions itself as producing studio-quality results, claiming audio fidelity of 44.1kHz. In practical terms, this suggests the audio is clear enough for broadcasting and streaming standards. The inclusion of features like a Vocal Remover and an MP3 to WAV converter further indicates an intention to support post-production workflows, allowing users to refine the generated assets or integrate them into larger projects with higher audio standards.
Observations On Commercial Usability And Licensing Rights
One of the most pragmatic features of the platform is its stance on intellectual property. The assurance of 100% royalty-free content addresses a major pain point for digital creators. By granting full ownership and commercial rights to the user, the platform mitigates the risk of DMCA strikes that frequently plague content on platforms like YouTube and Twitch. This legal clarity is often just as valuable as the audio quality itself, as it provides peace of mind for businesses incorporating these assets into advertising or product demonstrations.
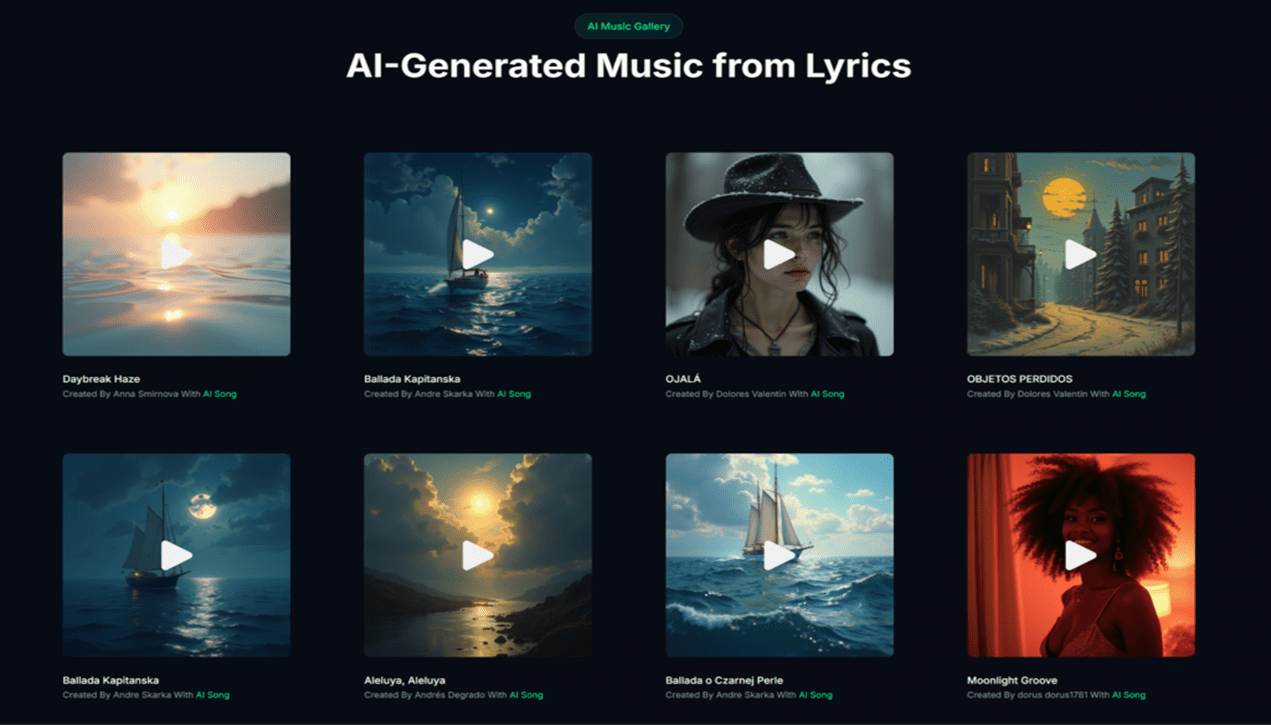
Understanding Current Limitations In AI Musical Expression
Despite the capabilities, it is important to approach AI music generation with realistic expectations. While the system can mimic genres and structures effectively, the “human touch”—the subtle imperfections and emotional nuances of a live performance—may vary. Users might find that complex emotional transitions or highly specific structural changes require multiple attempts or iterations to perfect. The technology is best viewed as a powerful assistant that generates a strong foundation or a complete background track, rather than a total replacement for the artistry required in top-tier musical masterpieces.