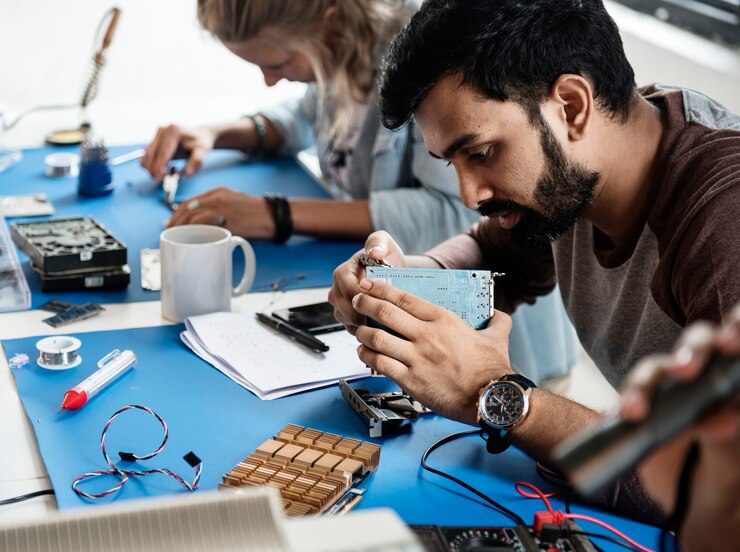
Navigating the Circuit: Unveiling Challenges and Clever Solutions in PCB Assembly
- 1 PCB Assembly
- 1.1 Miniaturization and Component Density
- 1.2 Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Challenges
- 1.3 Thermal Management
- 1.4 Automated Assembly vs. Manual Assembly
- 1.5 Component Obsolescence
- 1.6 Quality Control in Assembly
- 1.7 Environmental Impact and Regulations
- 1.8 Testing and Inspection Challenges
- 1.9 Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio-Frequency Interference (RFI)
- 2 Conclusion
In the complicated world of making electronics, the important step of putting together Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) shows how technology keeps advancing. Due to the increasing need for smaller and better electronic devices, the difficulties in putting together circuit boards have become more complex.
PCB Assembly
This article is all about exploring nine points about PCB assembly. It talks about the challenges and the solutions that have been found to overcome them.
Miniaturization and Component Density
The constant push for smaller devices makes it harder to fit more and more parts into limited space. Making things smaller and putting more parts close together causes problems like heat, signal interference, and more difficult soldering. To overcome these challenges, we need to use advanced ways of putting things together, use very small parts, and try out new ways of packaging things in 3D. This will help us navigate through this complex situation successfully.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Challenges
The arrival of surface mount parts brings difficulties with accuracy when putting them in place, especially because the components are getting smaller. Dealing with these difficulties requires using advanced vision systems and machines to place components accurately. The careful balance between accuracy and using machines is very important for getting the best results in surface mount technology.
Thermal Management
With the increased power density in modern electronics, it is important to effectively manage heat. Getting too hot can seriously damage the parts. Using new and creative ways to cool things down, like heat sinks, special pads, and advanced circuit board designs, becomes important to eliminate heat in the best way possible. This increased attention to thermal management focuses on the delicate balance needed to ensure electronic parts last long and work well.
Automated Assembly vs. Manual Assembly
The never-ending problem of deciding between automatic and manual PCB assembly methods depends on how many products need to be made and how complicated they are. Finding the right balance between using machines for large-scale production and relying on human workers for complex tasks is an important strategic decision. This detailed way of doing assembly processes focuses on making careful decisions to make manufacturing more efficient and cost-effective.
Component Obsolescence
The fast development of electronic parts brings up the possibility of becoming outdated. Successfully handling component obsolescence requires careful planning. This involves identifying possible problems and building strong relationships with different suppliers. This flexible approach includes always studying the market, forming important partnerships, and creating smart ways to buy things to reduce the risks of parts becoming outdated.
Quality Control in Assembly
Maintaining high-quality standards is always difficult. Using Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection technologies is important to ensure solder joints are of good quality and find defects that can’t be seen with just our eyes. This increased attention to providing things that are good shows the importance of keeping the final PCB working well and trustworthy.
Environmental Impact and Regulations
It is becoming more important to follow environmental rules and reduce the impact of PCB assembly on the environment. Following the rules of RoHS, using soldering without lead, and using materials that are good for the environment are important steps in dealing with these problems. This way of looking at environmental sustainability in PCB assembly shows how technology and responsible manufacturing are connected.
Testing and Inspection Challenges
Making sure that the assembled PCBs work properly is very important. In-circuit testing (ICT) and functional testing are very important for finding defects. Improvements in testing methods, like flying probe testing, make diagnostic processes more accurate and efficient. This detailed testing and checking process highlights the careful approach needed to ensure the final product is reliable and works well.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio-Frequency Interference (RFI)
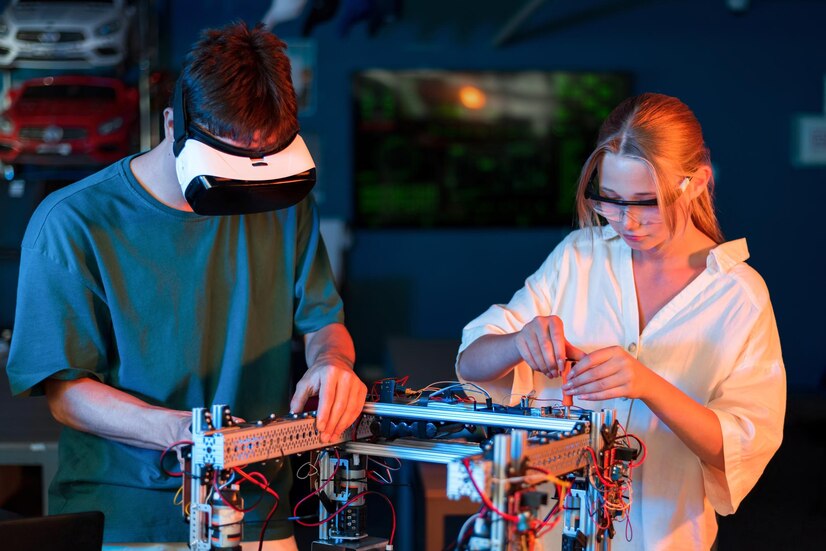

In a time when devices are more connected, it’s important to deal with the problem of reducing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio-Frequency Interference (RFI). It is important to use shields and filters and follow strict EMC rules to reduce interference. This detailed study of EMI and RFI reduction focuses on the complex engineering methods needed to ensure everything works smoothly in a world where electronic devices are more connected than ever.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex world of PCB assembly requires skillfully tackling various difficulties. The electronics manufacturing industry is about finding clever solutions, from making things smaller to managing the supply chain.
As people continue to want small and powerful devices, how we make circuit boards keeps improving. This shows how we develop new ideas and solve problems in this exciting field.