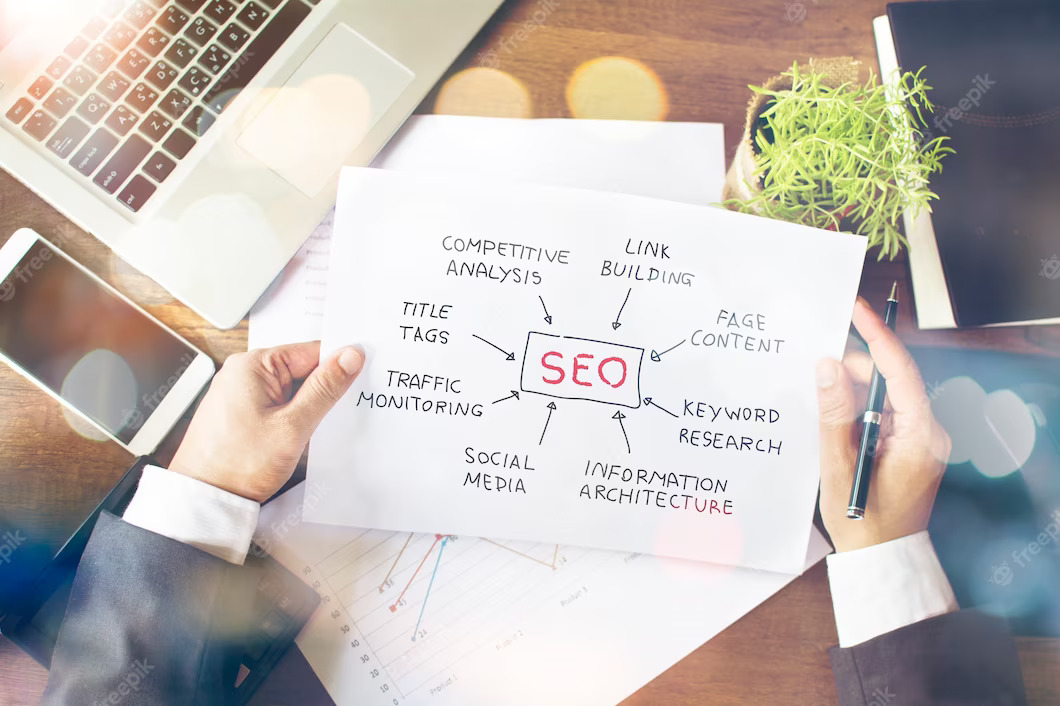
What Is Crawlability And How To Improve Website SEO With It
- 1 What Is Crawlability?
- 2 Crawlability: Why it matters
- 3 Six ways to improve the crawl ability of websites
- 3.1 Set up sitemap:
- 3.2 Reduce duplicate content:
- 3.3 Use a Robot.txt file:
- 3.4 Responsive design:
- 3.5 Fix broken links:
- 3.6 Reduce redirects:
- 4 Detail Video on How to make Google Crawl And Index Your Website Immediately
- 5 Conclusion
During the past few years, search engine technology has become more sophisticated than ever, especially in the area of search engine bots.
Google and other search engines have invested much money in improving their bots’ ability to read pages and index fresh content.
With this being said, web admins and SEO marketers should pay closer attention to website crawlability.
This article will explore everything related to crawlability and how to improve it to increase site visibility on Google.
What Is Crawlability?
Crawlability is the ability of search engine bots to read and index a website’s pages.
It can run on single or multiple URLs at once and can be triggered by several different events, including user requests, new links being added, or old pages being updated.
During the crawl, the search engine downloads files from the site and analyzes them for content and structure.
The search engine then stores this information for future reference in its index.
This process allows it to return relevant results when someone searches for specific terms on its platform.
Crawlability: Why it matters
Crawlability matters because it is the core of SEO. Google uses it to determine how healthy websites are optimized for its search engine.
If a site is not crawlable or has poor crawlability, it will see a drop in rankings and traffic.
This can be due to technical issues, such as broken links or duplicate content, but it can also happen because Google’s algorithms have changed and the website has not kept up with its constant updates.
This becomes detrimental to online marketing efforts if the web admin aims to attract organic users.
Six ways to improve the crawl ability of websites

Set up sitemap:
A sitemap is a file that lists all of the pages on the website and gives search engines information about each page, such as its title and last modified date. Search engines use this information to crawl websites more efficiently.
The sitemap can be manually submitted to the search console using tools like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
Copy the link of the XML sitemap through the third-party tool and visit Google Search Console. Head to the sitemap section, paste the link inside the “Add a new sitemap box,” and click “Submit.”
Reduce duplicate content:
Duplicate content refers to multiple page versions with identical or similar content.
For example, if you have two pages with the same content, one is called “home,” while another is called “home2,” this is considered duplicate content.
Google’s bots will try to handle this by indexing only one version or redirecting users to whichever version they think is most relevant.
If the website has any duplicate content, it should be removed and replaced with canonical tags (which tell Google which version it should index).
Use a Robot.txt file:
The Robots.txt file is an open standard for controlling robot behaviour on websites and servers.
In other words, it’s a set of rules for how bots should interact with the website so that they don’t cause problems like indexing too many pages or crawling duplicate content.
With the Robot.txt file, you can block entire sections of your site from being indexed or allow search engines to crawl only certain parts of your site.
For example, suppose you have an e-commerce store that sells seasonal or discontinued products.
In that case, you may want to exclude them from search results so potential customers aren’t disappointed when they see no products available on those pages.
Responsive design:
Responsive web design (RWD) makes the site more accessible and easier to read across different devices.
It adjusts the content to fit the device on which it’s viewed, making it easier for Googlebot to view the site and rank it for related searches.
Responsive design is fundamental for mobile optimization because Google has confirmed that it considers mobile-friendliness a ranking factor.
If a website or blog isn’t mobile-friendly, it misses out on massive traffic because Google is boosting its algorithm to favour mobile-friendly websites.
Fix broken links:
Broken links can lead to crawling issues because Googlebot may try to follow those links, but none of them will go anywhere.
There are two different types of broken links: “soft 404” pages (which can be detected by looking at the status code) and actual 404 pages (which don’t have a 200 OK response code).
If the website has 404 pages, it should be fixed as soon as possible so that Googlebot doesn’t waste time trying to access them.
Reduce redirects:
Redirects are an ordinary and necessary part of any website’s development.
Redirects allow website owners to move pages around and update links to reflect new URLs. However, too many redirects can affect your site’s crawlability.
Redirect chains occur when multiple redirects lead to the same page or when one redirect leads to another redirect that leads back to where the chain began.
This is problematic because it confuses search engine bots, which may be unable to crawl all your content if they get stuck in a redirect loop. It also makes it difficult for users to navigate your site.
Detail Video on How to make Google Crawl And Index Your Website Immediately
Conclusion
At this point, it is safe to say that crawlability is here to stay, and all websites should be designed with that in mind from the start.
This list of best practices can help optimize a site for better crawlability or at least minimize any negative impact on your crawl budget.