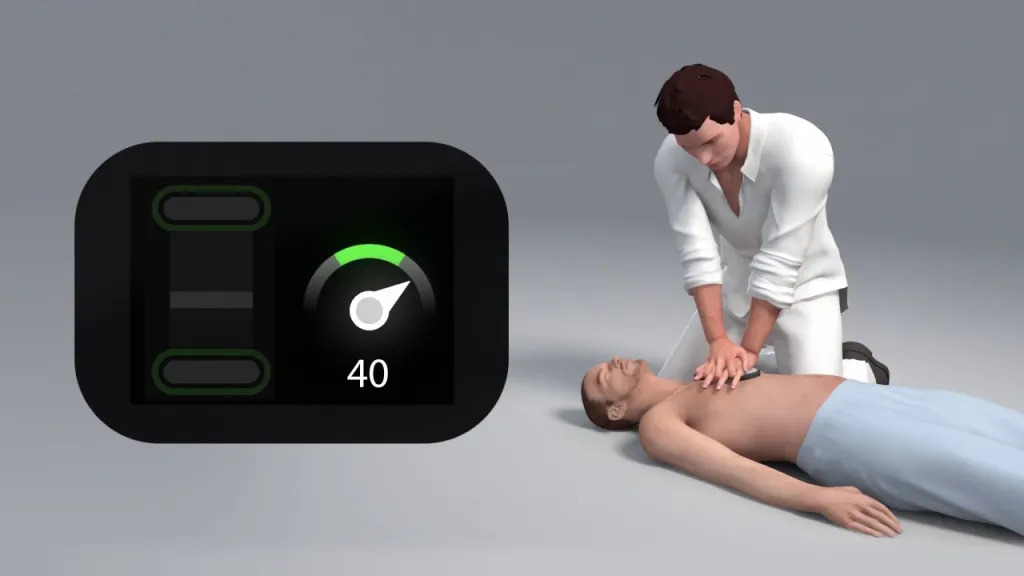
What Does A Chest Compression Feedback Device Monitor?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving procedure that includes chest compressions in the case of a cardiac arrest. Chest compressions increase the likelihood of survival by keeping blood pumping to the brain and heart. But performing chest compressions correctly and consistently can be difficult, and it’s hard to tell if they’re working without proper feedback. Medical personnel, first responders, and onlookers can benefit from using a chest compression feedback device to assess CPR’s effectiveness. Compression depth, pace, and recoil are just variables for which these gadgets can provide real-time feedback. Let’s look at what a chest compression feedback device tracks in further detail.
Chest Compression Feedback Device Monitor: What It Tracks?
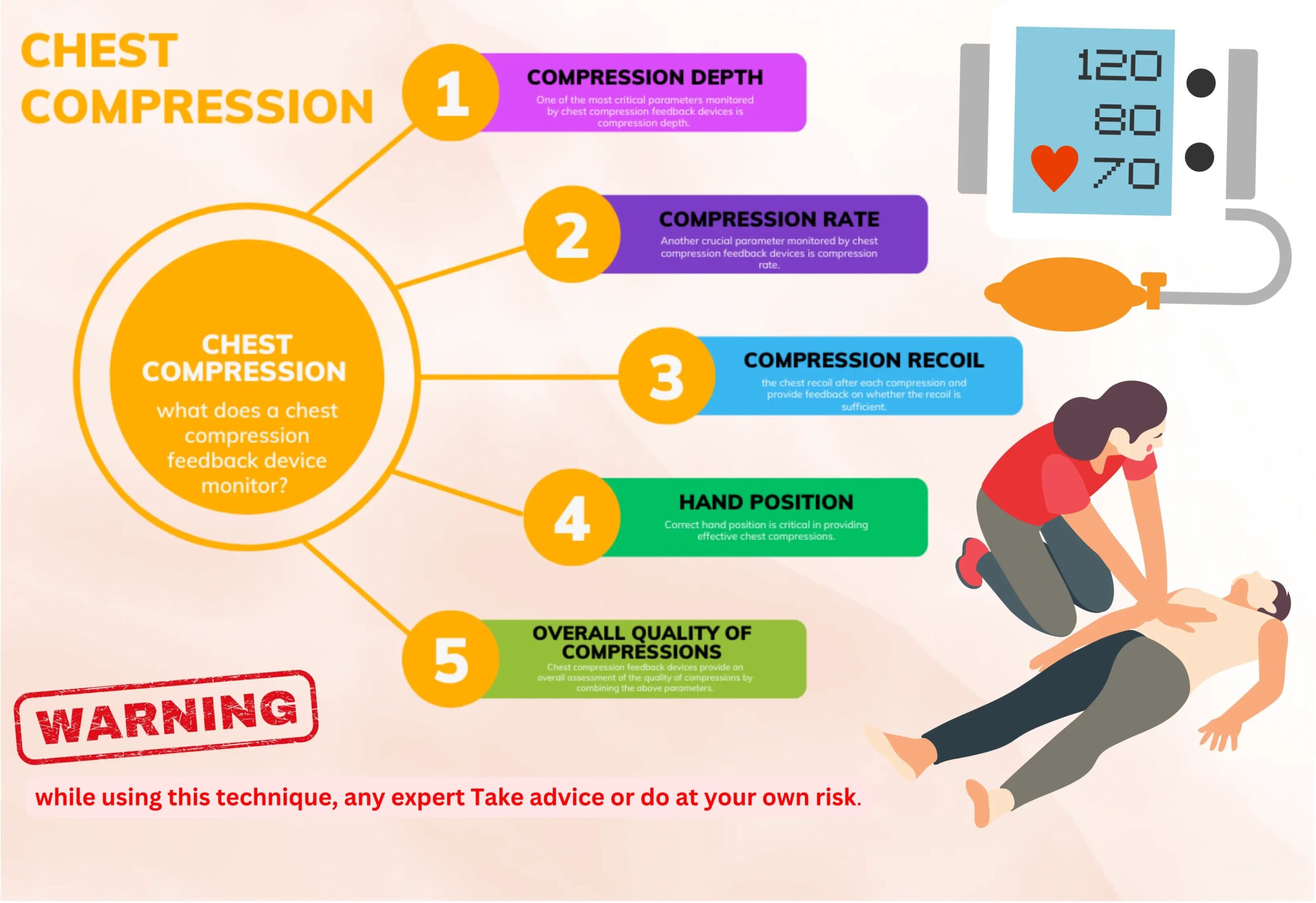
Pressure of Compression
The depth of chest compressions is one of the most important metrics a chest compression feedback device can track. When used on an adult, the gadget may measure chest compression depth and give feedback on whether or not it is within the recommended range of 2-2.4 inches (5-6 cm). Deeper compressions can cause internal injuries or damage to the chest, while shallower compressions may not generate enough blood flow.
Rate of Compression
Another vital indicator that a chest compression feedback system can track is the compression rate or the number of compressions performed per minute. Between 100 and 120 compressions per minute are where you want to be. Device measurements of compression rates can indicate whether or not those rates are optimal. Inadequate filling of the heart chambers between compressions can be caused by a compression rate that is either too slow or too quick.
Placement of Hands
Chest compressions only work if the hands are in the right place. The hand should be positioned in the middle of the chest, between the nipples, and the chest compression feedback device will let you know if you’re off. Improper hand placement during compressions may result in inadequate pressure on the chest.
Time Disrupted
The time between chest compressions is known as the “interrupted time” in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Any interruptions must be minimal when trying to maximize blood flow. The chest compression feedback device can track how often compressions are interrupted and give that information to medical staff, first responders, or onlookers to help them improve their performance.
Ventilation
Ventilation, or giving the person in cardiac arrest rescue breaths, is a crucial part of CPR. The chest compression feedback device can feed back the number of breaths supplied and the time between breaths. In addition, it can tell you if the ventilation rate is reasonable given the patient’s age, size, and health.
Resuscitation Percentage: CPR
The term “CPR fraction” describes the ratio of the time spent performing chest compressions to the total time spent performing CPR. The CPR fraction can be monitored using the chest compression feedback device, which also provides input on the duration of compressions.
Alternatives Of The Chest Compression Feedback Device Monitor
Even though chest compression feedback devices are a great way to check how well chest compressions work during CPR, they may only be available in some places or situations. In these situations, there are other ways to keep track of chest compressions during CPR, such as:
Visual Feedback
Seeing the chest rise and fall with each compression is a form of visual input. This method helps ensure that the amount of compression and the recoil are right. However, it might not give true information about the compression rate and when the compression was stopped.
Manual Monitoring
During CPR, manual tracking means checking the pulse and other signs of blood flow. Although this method may not give feedback on the specifics of chest compressions, it can help determine how well CPR works overall.
Audio Feedback
Audio feedback includes using a metronome or another sound-making device to give chest compressions a steady beat. This method can help ensure that the compression rate is between 100 and 120 per minute, which is suggested.
Simulation Training
CPR skills are practised on a manikin or computer during simulation training. This method can provide an accurate cardiac arrest simulation, let medical professionals, first responders, or bystanders practice CPR, and give them feedback from trainers or instructors on their technique.
Conclusion
There are several applications for chest compression feedback devices beyond just teaching CPR. Once you’ve practised with the device, it may only be obvious how much force is needed for chest compressions, but they can help you figure that out. They are also helpful in instructing older people and people with disabilities in CPR; if someone falls and hits their head on a hard surface like concrete or tile, it can be dangerous for them to attempt CPR without first learning the proper technique.