Everything About a Wi-Fi Network
- 1 What is Wireless Fidelity?
- 2 How Does WiFi Work?
- 3 Components of a WiFi Network
- 3.1 Wireless Router
- 3.2 Wireless Access Point
- 3.3 Wireless Adapters
- 3.4 Wireless Bridge
- 3.5 Wireless Controller
- 4 How to Extend the WiFi Range?
- 4.1 WiFi Range Extenders/Repeaters
- 4.2 Mesh WiFi Systems
- 4.3 Router Placement
- 4.4 Powerline Adapters
- 4.5 Upgrade Your Router
- 4.6 WiFi Boosters
- 5 Conclusion
- 5.1 FAQs:
- 5.1.1 What is WiFi?
- 5.1.2 How does WiFi work?
- 5.1.3 What are the main components of a WiFi network?
- 5.1.4 What are the different WiFi frequency bands?
- 5.1.5 What are WiFi standards, and how do they affect performance?
- 5.1.6 How can I extend the range of my WiFi network?
- 5.1.7 What is the difference between a WiFi range extender and a mesh WiFi system?
- 5.1.8 How can I improve WiFi signal strength in my home?
- 5.1.9 Can I connect devices without built-in WiFi capabilities to a WiFi network?
- 5.1.10 What is a wireless bridge, and how is it used in WiFi networks?
- WiFi, or Wireless Fidelity, is a technology that enables wireless internet access using radio waves.
- It operates on frequencies of 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz, offering high-speed connections with various standards like 11b, 11a/g, and 11n.
- Components include routers, access points, adapters, bridges, and controllers, with options to extend range using extenders, mesh systems, powerline adapters, and boosters.
What is Wireless Fidelity?
Wireless Fidelity, commonly known as WiFi, is a type of network technology that uses radio waves to provide internet access to users wirelessly. It provides a high-speed and bandwidth network connection and has a higher range as compared to Bluetooth and infrared.
WiFi is the most commonly used network type in the current century. Most electronic gadgets, including cell phones, laptops, tablets, and desktops, are fitted with the technology that renders them able to use WiFi.
How Does WiFi Work?
WiFi is more similar to an FM or AM radio than we may think. It uses radio waves to transfer information and data, just like a radio. The only difference is that WiFi is a 2-way channel, unlike FM and AM radio, which are one-way channels. The WiFi router is outfitted with specialized hardware to broadcast and receive information simultaneously.
WiFi uses two types of frequencies, i.e., 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz, to minimize the noise and interference due to other broadcasting media, such as TVs and radio. However, it may still face interference due to other electronic devices as well as the weather, which may cause some decline in its speed and efficiency.
If we talk about its speed, it uses different set standards that have seen some evolution over time as well.
Here are these standards:
- 11b is the oldest and the least expensive standard. It is also the slowest of all.
- 11a and 802.11g replaced the previous standard and provided a faster and more efficient network.
- 11n is the latest standard that offers better speed and longer range as compared to others
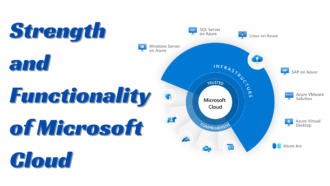
Components of a WiFi Network
There are 5 common components of a WiFi network, which are briefly described below:
Wireless Router
A wireless router serves the purpose of both a router and a wireless access point (WAP). The router directs the traffic from the connected devices to the internet and vice versa, whereas a WAP allows the devices to connect to the network.
Wireless Access Point
A wireless access point or WAP allows a wired connection to connect the devices wirelessly. It is an extension of the wireless capabilities of a router that allows it to provide a secure wireless network to the surroundings.
Wireless Adapters
Wireless adapters allow a piece of hardware that is installed in computers, laptops or other electronic devices to enable them to connect to a WiFi network. They are also called network interface cards (NICs).
Wireless Bridge
A wireless bridge allows two different networks to connect and communicate with each other wirelessly. It allows one network to share its internet connection with the other. This provides internet access to the devices connected to the other network.
Wireless Controller
A wireless controller is generally used in larger WiFi deployments which provides a centralised management and control of multiple access points. This is commonly used in hospitals, campuses and Office WiFi Solutions.
How to Extend the WiFi Range?
WiFi Range Extenders/Repeaters
These devices are used to extend one network over a larger area. They pick up the WiFi signal of the network, boost it and transmit it over the area. They need to be placed within the range of your WiFi network.
Mesh WiFi Systems
These systems create a network of multiple nodes that are interconnected to each other. This type of system provides a seamless and smooth network coverage throughout the space. These nodes communicate with each other and to the router automatically to ensure optimal performance. These devices are suitable for event WiFi solutions.
Router Placement
You can also position your router optimally to increase its propagation. You can try elevating it to avoid obstacles and changing the direction of its antenna to enhance its coverage.
Powerline Adapters
Powerline adapters use the electrical wiring of an establishment to transmit data and information. They provide a wired connection to create multiple WiFi hotspots over a large area.
Upgrade Your Router
Modern WiFi routers are outfitted with cutting-edge technology that offers wider coverage and more signal strength to a WiFi network. You can check your router and replace it with the latest one if it is too old.
WiFi Boosters
WiFi boosters are designed to receive your WiFi signals and transmit them over a large area after amplifying their strength. They allow the signal to cover a wider area by increasing the strength of the signals.
Conclusion
WiFi, or Wireless Fidelity, has revolutionized the way we access the internet by providing wireless connectivity through radio waves. Its versatility and ubiquity have made it an integral part of modern life, powering a wide range of devices and applications. With its ability to deliver high-speed connections and its constant evolution through various standards and technologies, WiFi continues to play a crucial role in shaping our digital landscape. As we continue to rely on wireless connectivity for work, communication, entertainment, and more, understanding how WiFi works and how to optimize its performance becomes increasingly important for ensuring seamless connectivity in our increasingly connected world.
FAQs:
What is WiFi?
WiFi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a wireless networking technology that allows devices to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables.
How does WiFi work?
WiFi works by transmitting data through radio waves between a router (or access point) and wireless-enabled devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
What are the main components of a WiFi network?
The main components include a wireless router, wireless access points, wireless adapters, wireless bridges, and wireless controllers.
What are the different WiFi frequency bands?
WiFi operates on two primary frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz, each offering different advantages in terms of range and speed.
What are WiFi standards, and how do they affect performance?
WiFi standards such as 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n define the technology’s capabilities, including speed and range. Newer standards typically offer faster speeds and better performance.
How can I extend the range of my WiFi network?
You can extend WiFi range using devices like range extenders, mesh systems, powerline adapters, or by upgrading to a newer router with enhanced coverage.
What is the difference between a WiFi range extender and a mesh WiFi system?
A range extender amplifies existing WiFi signals, while a mesh WiFi system creates a network of interconnected nodes to provide seamless coverage throughout a space.
How can I improve WiFi signal strength in my home?
You can improve WiFi signal strength by positioning the router optimally, avoiding obstacles, upgrading the router, or using WiFi boosters to amplify signals.
Can I connect devices without built-in WiFi capabilities to a WiFi network?
Yes, you can use wireless adapters or network interface cards (NICs) to enable devices without built-in WiFi to connect to a WiFi network.
What is a wireless bridge, and how is it used in WiFi networks?
A wireless bridge connects two separate networks wirelessly, allowing them to communicate and share internet access. It is useful for extending connectivity between distant locations.