The Advantages and Disadvantages of Glass-Filled Nylon Filaments
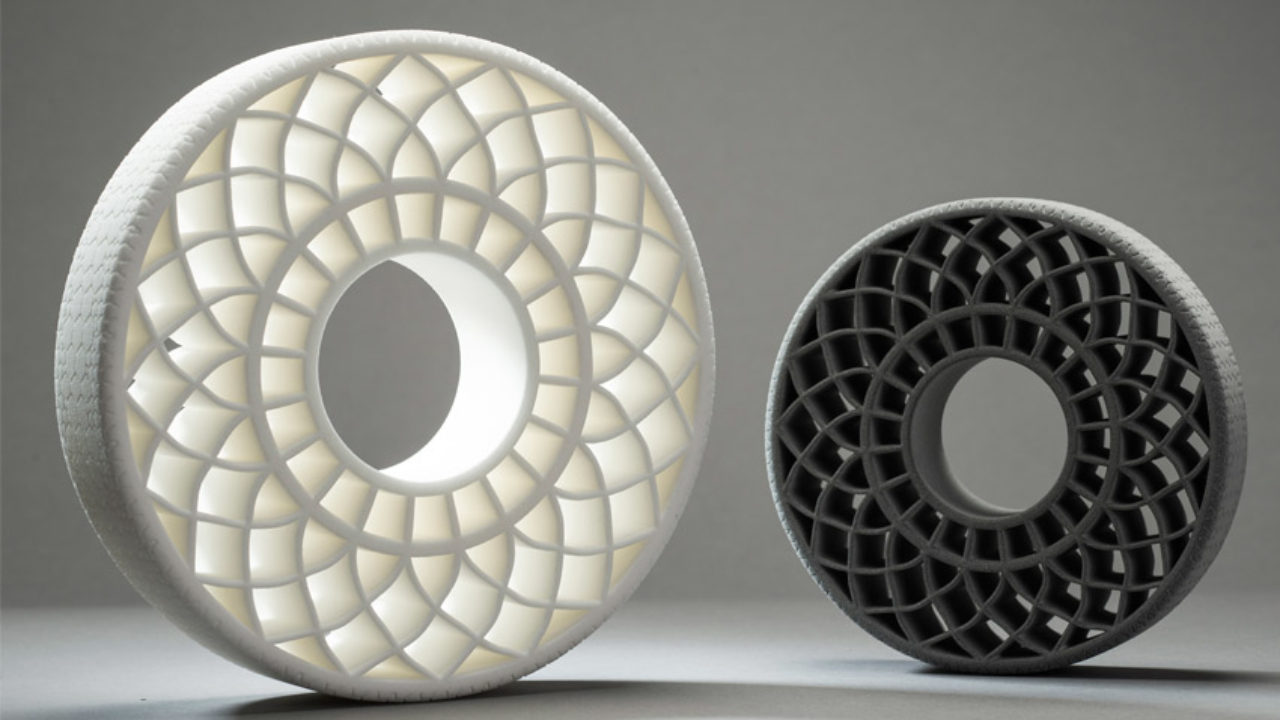
Glass-filled nylon is a strong and heat-resistant material widely used in engineering. It is a synthetic polyamide thermoplastic with numerous advantages due to its unique properties.
This material is produced by combining powdered glass with nylon resin or extruding plastic with glass fibres. Another application of glass-filled nylon is in 3D printing, where glass spheres can be added to the base powder in different proportions. Adding glass to nylon has brought about a paradigm shift in engineering.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Glass-Filled Nylon Filaments
There are various advantages of using glass-filled nylon, which are given below:
- Significant improvement in strength and rigidity – When glass is added to nylon, it becomes substantially more robust, more complex, and more rigid than regular nylon.
- Glass-filled nylon exhibits higher resistance to creep, which is the tendency of a material to deform over time under constant stress.
- It also offers better dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size more effectively when exposed to temperature fluctuations.
- Additionally, glass-filled nylon demonstrates increased wear resistance, making it more durable and long-lasting than regular nylon.
- It can withstand higher maximum service temperatures, making it suitable for applications that involve elevated temperatures.
- Enhanced ability to withstand external forces and resist deformation.
- It has superior tensile strength and can withstand higher pulling or stretching forces without breaking.
- Glass-filled nylon is stiffer, which resists bending or flexing more effectively.
- It has a substantially lower thermal expansion rate, meaning it is less likely to change shape or size when exposed to temperature changes. This property is advantageous in applications where dimensional accuracy is crucial.
- It exhibits good fatigue strength, allowing it to endure repeated stress cycles without failure.
- It possesses high mechanical damping properties, which means it absorbs and dissipates mechanical energy, reducing vibrations and noise.
These characteristics make it an ideal material for parts subjected to high static loads in high-temperature environments.
Disadvantages of Glass-Filled Nylon Filaments
Despite its many advantages, glass-filled nylon also has some disadvantages, which are as follows:
- Significantly higher cost than regular nylon – Adding glass fibres increases the production cost, making glass-filled nylon more expensive.
- Glass-filled nylon tends to be more brittle than regular nylon. This means it is more prone to cracking or breaking under impact or excessive stress.
- The glass filler in glass-filled nylon is quite abrasive, which can cause increased wear and tear on cutting tools and other equipment used in machining processes. It can also lead to the erosion of mated parts due to increased friction.
- Glass-filled nylon is heavier than regular nylon, which can disadvantage weight-sensitive applications.
- Glass-filled nylon has significantly weaker weld lines, which are the lines formed during the fusion of molten plastic in injection moulding. These weaker weld lines can compromise the structural integrity of the final product.
- Glass-filled nylon exhibits anisotropic properties, meaning it shrinks and expands unevenly. This could pose challenges in achieving dimensional accuracy and consistency in moulded parts.
In 3D printing, nylon materials are known for producing strong and durable parts suitable for both functional prototyping and end-use projects. Glass-filled nylons particularly outshine regular nylons concerning long-term wear resistance, higher stiffness, and superior heat deflection resistance.
Different glass-filled nylons can be used for selective laser sintering (SLS) and Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) 3D printing. All printed nylons, including glass-filled ones, exhibit high strength, stiffness, and temperature resistance levels. However, glass-filled nylons enhance performance, stiffness, and heat deflection.
In performance, PA66-GF30 and PA6-GF30 are nylon filaments infused with 30% glass fibres. Offer enhanced strength, rigidity, and heat resistance compared to standard nylon filaments. They are ideal for applications that require high mechanical performance and dimensional stability in 3D printing projects.
In injection moulding, glass-filled nylon offers improvements over regular nylon in hardness, tensile strength, and dimensional stability. Adding glass fibres to nylon can enhance the material’s heat resistance and resistance to UV light.
Injection moulding projects benefit from the increased rigidity, improved hardness, superior tensile strength, increased creep resistance, more excellent dimensional stability, and high mechanical damping provided by glass-filled nylon.
It is important to note that nylon, particularly glass-filled nylon, can be more prone to warp due to non-linear shrinkage. Therefore, it is essential to select the appropriate type of nylon that suits the specific needs of a project. Moreover, working with glass-filled nylon can present dimensional challenges when dealing with semi-crystalline materials. Thus, it is necessary to carefully evaluate the trade-offs associated with using glass-filled nylon in each application.
In summary, considering the advantages and disadvantages of glass-filled nylon, glass-filled nylon provides numerous advantages and offers good mechanical properties, fatigue resistance, noise damping, and excellent bearing and wear resistance if handled carefully and correctly.