Supply Chain Optimization: Significance and Implementation
- 1 The Role of Specification Management in Supply Chain Efficiency
- 1.1 Challenges Addressed by Streamlined Specification Processes
- 1.2 Implementing Advanced Technology for Specification Handling
- 1.3 Impact on Supplier Collaboration and Communication
- 1.4 Future Trends in Specification Management for Supply Chains
- 2 Best Practices for Supply Chain Management
- 2.1 End-to-End Visibility:
- 2.2 Demand Planning and Forecasting:
- 2.3 Supplier Collaboration:
- 2.4 Inventory Optimization:
- 2.5 Warehouse Efficiency:
- 2.6 Transportation Management:
- 2.7 Technology Integration:
- 2.8 Continuous Improvement:
- 2.9 Risk Management:
- 2.10 Sustainability Initiatives:
- 2.11 Collaboration and Communication:
- 2.12 Compliance and Regulatory Considerations:
- 3 Wrapping up
Supply chain management is one of the most important aspects of running a supply-based business. However, optimizing the supply chain mechanism in your organization can be tricky and laborious at times.
In this blog, we will discuss some key factors to focus on while optimizing your organization’s supply chain process.
So, buckle up, and let’s get started.
The Role of Specification Management in Supply Chain Efficiency
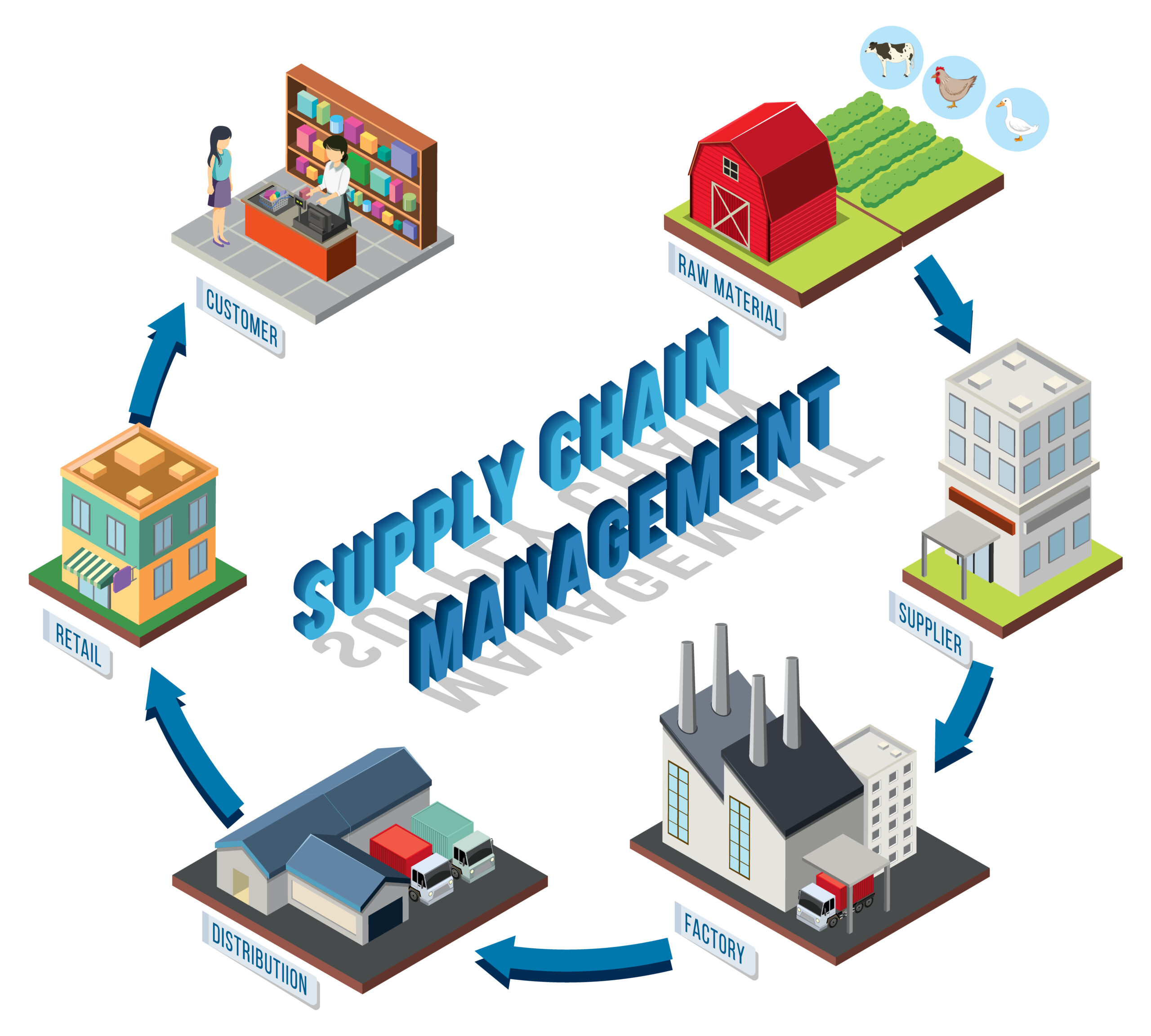
Effective specification management is critical to improving supply chain efficiency. It is the principal centre for documenting and communicating precise product requirements, standards, and changes across the supply network.
Companies use specification management software to eliminate errors, shorten lead times, and improve product quality. This entails assuring uniformity in materials, manufacturing, and quality standards and facilitating smoother coordination among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
Finally, good specification management streamlines operations reduces risks, and improves overall supply chain performance, setting the groundwork for agile and responsive corporate operations in today’s competitive market.
Challenges Addressed by Streamlined Specification Processes
- Ambiguity and Misinterpretation: Clear specifications minimize misunderstandings, reducing the chances of misinterpretation in product requirements.
- Time Delays and Revisions: Efficient specification processes diminish time-consuming revisions, ensuring quicker decision-making and project progression.
- Inconsistency in Quality: Standardized specifications maintain consistent quality standards across products and suppliers, averting discrepancies.
- Communication Breakdowns: Streamlined processes foster better stakeholder communication, preventing information leaks and enhancing collaboration.
- Regulatory Compliance Issues: Rigorous specification management ensures adherence to industry regulations, reducing compliance-related risks and penalties.
Implementing Advanced Technology for Specification Handling
Implementing cutting-edge technology transforms the environment of specification management inside supply chains. Such software solutions and digital platforms enable real-time collaboration by allowing stakeholders to access, change, and synchronize requirements seamlessly.
Most of the reliable cloud-based solutions are scalable and accessible. This allows for distant involvement and quick changes. As a result, AI-driven analytics speed up data processing while pricing insights for better decision-making.
Additionally, integration with IoT devices also improves monitoring and traceability, assuring accuracy in tracking specs throughout the manufacturing cycle.
Adopting such advanced technology speeds up procedures and improves accuracy, transparency, and adaptability. This fundamentally alters how specifications are handled throughout complicated supply chain networks.
Impact on Supplier Collaboration and Communication
Efficent specificational management improves supplier collaboration and communication within supply chains dramatically.
For example, clear and easy specification guidelines promote a shared understanding among suppliers, reducing misunderstanding and encouraging confidence. This makes information sharing more efficient and minimizes errors and delays.
Furthermore, collaborative platforms can facilitate real-time interactions, allowing for rapid feedback and query resolution.
Such transparency helps maintain strong collaborations by enabling managers to engage and align on common goals actively.
As an organization ensures easier interaction and creates the framework for a more agile and synchronized supply chain ecosystem, supply chain functions become more refined and productive.
Future Trends in Specification Management for Supply Chains
Future trends in supply chain specification management point to ongoing technological advancement.
As machine learning technologies evolve, AI-powered automation is set to improve data processing and decision-making while also optimizing specification handling.
Integrating blockchain into supply-chain systems can enhance traceability and security, assuring tamper-proof standards across the supply chain.
Similarly, focusing on sustainability can also help with eco-friendly specification management that considers environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Furthermore, technological convergence can help pave the way for more integrated and interoperable specification management systems.
Best Practices for Supply Chain Management

End-to-End Visibility:
Incorporating advanced technologies, such as IoT, RFID, and sensors, facilitates real-time tracking of inventory, shipments, and production processes. Additionally, implementing robust data analytics tools provides comprehensive insights across the entire supply chain. This visibility enables informed decision-making and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Demand Planning and Forecasting:
Collaboration with suppliers, distributors, and retailers is crucial to enhance demand forecasting accuracy. Organizations can develop more reliable demand planning models by sharing and leveraging various data sources, including historical data, market trends, and customer feedback. Moreover, considering external factors such as economic conditions and geopolitical events contributes to a more holistic and accurate forecasting approach.
Supplier Collaboration:
Building solid relationships with key suppliers is foundational to effective supply chain management. Employing supplier scorecards allows organizations to assess performance based on critical metrics such as quality, lead times, and reliability. Furthermore, implementing dual-sourcing strategies minimizes the risks associated with dependency on a single supplier, promoting resilience within the supply chain.
Inventory Optimization:
Efficient inventory management, including the adoption of just-in-time (JIT) principles, minimizes holding costs and mitigates the risk of stockouts. Implementing ABC analysis to categorize inventory based on importance ensures that resources are allocated appropriately. Regular reviews and adjustments to inventory levels in response to demand patterns and market changes are essential for optimizing inventory management.
Warehouse Efficiency:
Optimizing warehouse operations involves strategic layout planning and the integration of automation technologies. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) contribute to real-time tracking and improved control over inventory. Through training programs, organizations can enhance the efficiency of warehouse staff, reducing errors and improving overall operational effectiveness.
Transportation Management:
Route optimization software and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) help minimize transportation costs and delivery lead times. Exploring multimodal transportation options provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness in moving goods. Collectively, these strategies contribute to streamlined transportation management within the supply chain.
Technology Integration:
Digital transformation, facilitated by the integration of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems, enhances overall efficiency and communication. Exploring emerging technologies like blockchain adds transparency and security to supply chain operations.
Continuous Improvement:
Establishing a culture of continuous improvement involves regular reviews and optimizations of existing processes. Performance assessments and feedback from stakeholders help identify areas for enhancement. Implementing Lean and Six Sigma methodologies aids in waste elimination and the overall streamlining of supply chain operations.
Risk Management:
Identifying and mitigating risks within the supply chain is essential for maintaining business continuity. This involves developing contingency plans and diversifying suppliers to reduce dependencies. Regular geopolitical, economic, and environmental risk assessments contribute to a resilient supply chain.
Sustainability Initiatives:
Integrating sustainable practices into the supply chain aligns with environmental and social responsibility goals. This includes considerations such as eco-friendly packaging, energy-efficient transportation, and ethical sourcing of materials, contributing to a more sustainable and socially conscious supply chain.
Collaboration and Communication:
Promoting collaboration among different departments and external partners enhances overall supply chain efficiency. Leveraging collaborative platforms and communication tools facilitates real-time information sharing, improving decision-making and responsiveness.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations:
Staying abreast of local and international regulations is crucial for compliance within the supply chain. Adhering to quality standards, safety regulations, and customs requirements ensures smooth and lawful operations. Regular updates and adherence to regulatory standards contribute to the overall success and resilience of the supply chain.
Wrapping up
Efficient specification management is the key to optimizing supply chain efficiency. Adopting cutting-edge technologies and encouraging collaboration signal a future of agile, resilient, and synchronized supply chains.

















